Internal capsule of the brain( capsula interna): structure. Anatomy of the brain
The inner capsule of the brain is a white substance, represented as a curved strip and located in the gap between the ganglia of the base of the subcortex. It consists of complete "conductors" - projection fibers, which provide a link between the brain itself and other further located areas of the central nervous system.
Anatomical structure of capsula interna
Isolate the anterior( located between the caudal nucleus of the reticular formation - nucleus caudatus and amygdala-nucleus lenticularis) and the posterior nucleus( between the visual zone of the thalamus - thalamus opticus and the same amygdala-nucleus lenticularis).In addition to genu capsulae internae( anterior and posterior thigh), there is also a knee. It is located in the area of inflexion of the capsule. 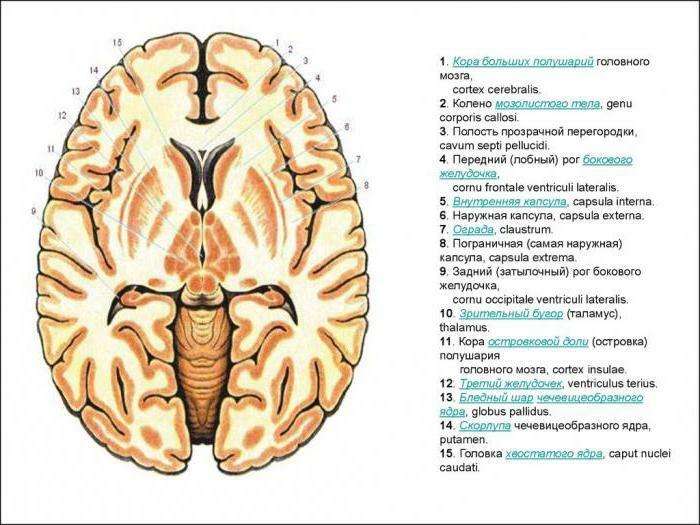
The inner capsule of the brain is important.
The main pathways passing through the white matter of the brain
Tractus cortico-bulbaris interacts between the cortex and the nuclei of the cranial nerves.
Tractus cortico-spinalis consists of central motor fibers, like the previous tract, and reaches the anterior horn of the spinal cord, passing through the front two thirds of the posterior hip area in such a way that the fibers for the upper limb are located in front, and in the rear for the lower extremities. What is an axon and a dendrite? About this further.
Tractus thalamo-corticalis pass from the visual boom to the cortex, being located behind the previous path.
Direct visual pathways starting from the primary centers of view of corpus geniculatum laterale, ending with the occipital lobe( radiatio optica) - the fasciola beam.
Starting from the area of the subcortex and ending with the primary auditory center in the temporal lobe( corpus geniculatum mediale), the auditory tract is located.
Tractus fronto-pontinus, that is, the frontal path, reaches the bridge and the cerebellum, while occupying the anterior thigh of the inner capsule.
The occipital-temporal tract( tractus occipito-temporo-pontinus) passes, respectively, between the cortex and the temporo-occipital region.
Tractus cortico-thalamici lies in the anterior and posterior thigh and connects the visual crescent with the bark. 
As the nerve fibers cross over in the course of their location, the diagnostic criterion will be the defeat of the opposite side of the limb, if this affects the sensitive fibers, then at the level of their overlapping in the region of the dorsal and medulla oblongata, and the motor nerves( pyramidal pathways) at their boundary.
With complete damage to the inner capsule of the brain, there is talk of a "three-hemi syndrome":
• Hemiplegia( lack of self-performed movements).
• Hemianesis( complete loss of sensitivity) on the opposite side of the body.
• Hemianopsia( blindness of both eyes, affecting half the field of view).
The axon and dendrite are the components of the neuron. Axon is a long process, the length of which can be several meters. They perform the function - transfer information from the body of the neuron to other cells of the central nervous system.
Dendrites of a neuron are called multiple nerve fibers, which are a collector of information, that is, transmit it to the body of the nerve cell. 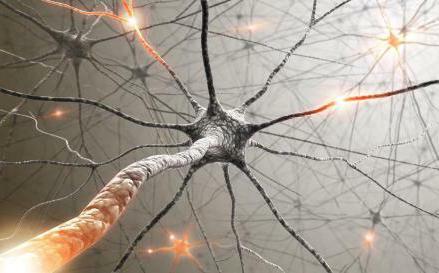
Hemiplegia
As a rule, there is the same percentage of involvement in this process of both the upper and lower limb. Often the paresis of the tongue and muscles of the lower part of the face develops along the central type.
Anatomy of the inner capsule of the brain is of interest to many.
hemianesthesia Half-character and more often affects the distal( lower) parts of the limbs. If the area is damaged above the visual hillock, such sensitivities may fall out, such as pain and temperature or muscle and joint and other types. Rough lesions are combined with a feeling of irradiation, fuzzy arrangement and the presence of aftereffects, that is, hyperpathy takes place. 
Hemianopia
Characterized by damage to the fibers that make up the Gràciolo beam with the observed aftereffect from the opposite side.
Most often, quite severe and complicated lesions are not observed on the part of the hearing aid, which is primarily due to the two-way localization of the pathways, so the sound that has entered the auditory canal, changing in momentum, reaches both the right and left hemispheres.
Depending on what part was affected by the traumatic impact, and on which part of the route is located there, we can predict the further development of the situation. Thus, when the region of the inner knee of the inner capsule of the brain and the anterior portion of the posterior thigh are affected, hemiplegia will be expressed in the absence of pathological changes on the part of the motor or any other sensitivity.
If the opposite part( posterior portion of the thigh) is affected, the effect will be reversed.
A group of white matter( centrum semiovale) is also distinguished, located between the ganglia and the cortex of the hemispheres. This site contains projection and association fibers. The first connect the cortical substance with the underlying parts, located almost perpendicular. They are represented by cortical and corticostemporal conductors.
What is interesting about the structure of the inner capsule of the brain?
Association beams interrelate different departments within one hemisphere. It can be either short( V-shaped), connecting adjacent gyrus, and long( fasciculus longitudinalis superior and fasciculus longitudinalis inferior, for example).To the variety of association are commissural fibers, which, unlike other types of fibers, interact outside the hemispheres, promoting their interaction.
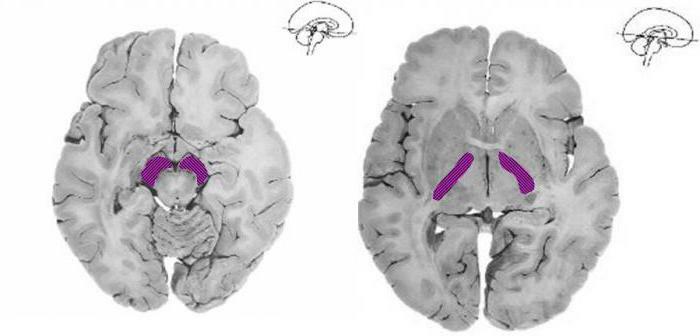
The corpus callosum
The corpus callosum is the most important and powerful bundle of all commissural fibers. This formation combines the same parts: the parietal of the right hemisphere with the same lobe only of the left hemisphere and so on. Also, corpus callosum participates in the formation of the olfactory tract, passing through the front and back white solderings.
Foci of white matter, localized on both sides( such as, for example, centrum semiovale, capsula interna), predispose to the occurrence of pseudobulbar disorders of both speech and swallowing, mainly due to pathological changes in the two tractus cortico-bulbaris. In addition, bilateral pyramidal symptoms join due to disturbances in the tractus cortico-spinales on both sides. Often, all add to the phenomenon of violent crying or laughing, other types of pseudobulbar disorder and hypomymia.
