Subungual melanoma: causes of onset, diagnosis and treatment
Melanoma of the nail or subungual melanoma( Latin "melanoma", from the ancient Greek "μέλας" - "black" + "-ομα" - "tumor") is a malignant disease that develops from specialized skin cells( melanocytes) that produce melanins. It occurs not only on the inside of the hand and the sole of the foot, but also on the nails( most often the fingernail of the thumb or foot is affected, but the damage to other nails and fingers is not excluded).

How common is it?
Among all cancers, the incidence of melanoma of the nail is about 3% in women, and in men - about 4%.Previously, it was always believed that subungual melanoma can occur mainly in elderly people, but now this malignant tumor has been observed increasingly in young people.
In comparison with other cancers, the growth of nail melanoma occurs much faster, since the body is very weak or there is no response at all to it. Therefore, according to statistics, after malignant tumors of the lungs this ailment takes the second place.
Types of
Several types of subungual melanoma stand out:
- developed from the nail matrix( a skin area located under the root of the nail, responsible for the production of new tissues);
- appeared from under the nail plate( the main part of the nail, protecting the soft tissue of the finger);
- evolved from the skin next to the nail plate.
Causes of development of nail melanoma
Nail melanoma is affected by people of all races, regardless of country of residence and status. In fact, at the present time, science has not fully established the causes of the appearance of this disease. However, it is possible to isolate the factors that influence the transformation of healthy cells into malignant cells. The risk groups are: 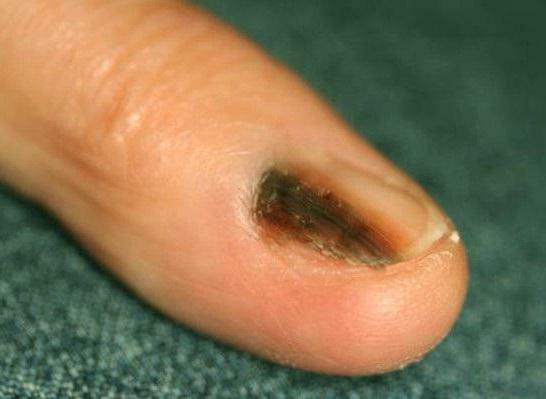
- people who have fair skin, blue eyes, lots of pink freckles and light or red hair;
- those who have a history of sunburn( even if they were received in childhood or adolescence);
- people in the family history of which were repeatedly recorded cases of subungual melanoma, are subject to this disease 3-4 times more often;
- people whose age is over 50;
- regularly exposed to ultraviolet rays( including artificial sunscreen equipment);
- suffer from a lack of vitamins, rest and have weak immunity, as well as those who work with corrosive media and chemicals fall into the risk zone. Next, find out what the melanoma looks like.
Signs of the disease
In most cases, with the progression of the disease, the symptoms of nail melanoma also change. Therefore, it is extremely important not to lose sight of the first signs characterizing the onset of malignant formation in time, because, as a rule, the early development of the disease is asymptomatic. But in later stages, the following signs begin to appear:

- Under the nail plate, there is a dark pigmented spot. This stain can look on the nail bed in the form of a longitudinal band. Sometimes the occurrence of melanoma of the nail can be preceded by a minor injury to the patient's finger, which did not turn to the doctor in time.
- As a rule, within a few weeks or months, the stain under the nail increases. It begins to change color to light or dark brown and becomes wider in the area of growth of the cuticle, and as a result can completely cover the entire area of the nail.
- Malignant new education begins to spread to the nail roller that surrounds the nail plate.
- Begin to appear bleeding ulcers and developing nodules, which lead to deformities, cracks and thinning of the nail plate. And also from under a fingernail pus starts to be allocated.
So, you already know what a melanoma looks like. The above signs will allow the doctor to suspect pathological destruction of epidermal tissues and the presence of this dangerous disease in the patient. In some cases, a specialist who examines a patient confuses a dermatological affliction with a panaritic infectious nature of origin and prescribes surgical sanitation of the affected skin surface.
The precious time that would have to be used for tumor therapy is lost, and the signs of cancer return again and with a more vivid manifestation of the clinical picture. 
Since very often neoplasms under the nail have no color, in half the cases of this disease, unfortunately, the external symptoms are noticed by patients too late. Melanoma of this kind of nail can be seen only if a nodule begins to form under the plate, which raises the nail up.
It should be noted that this disease is subject to the same degree of both hands and feet. If a malignant tumor has spread to the sole, then it provokes obvious discomfort during movement. In the early stages this disease is so asymptomatic that sometimes doctors confuse it with ordinary skin warts.
Stages of
So, we select all the stages of the nail melanoma:
- First there are lesions on the surface of the skin, the nail plate reaches a thickness of 1 mm, however, this does not cause concern to the patient.
- During the second stage, the subungual melanoma reaches a thickness of 2 mm and begins to spread along the nail plate, thereby changing the pigmentation. The stain expands while darkening while.
- After this, the malignant cells begin to spread to the nearest lymph nodes, and also the damage to the skin around the nail is often observed.
- At the fourth stage, metastases begin to appear in the liver, lungs and bones.
Everyone should remember that the symptoms of subungual melanoma are important in time to recognize.
Diagnosis of pathology
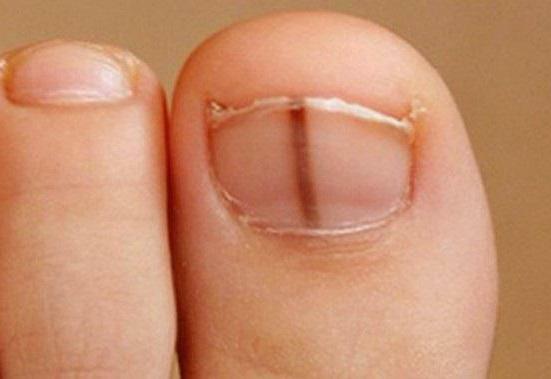
The reason for a visit to a specialist should be any pigmentation of the nail plate, especially if it increased in size( up to 3 mm or more), because the melanoma of the nail at an early stage often has ambiguous signs. To determine the malignancy of the neoplasm under the nail, qualified specialists use a dermatoscope - a special optical microscope used to scan the horny layer of the nail and skin to assess the pathological changes visually: the extent of spread, the size and thickness of the tumor. Next, you will learn how to distinguish the subungual melanoma from the hematoma.
Biopsy
If during the dermatoscopy the malignant origin of the tumor was detected, then the doctor prescribes an additional biopsy to remove the suspicious formation along with the area of the surrounding skin and to study in the laboratory a section of tissues under a more powerful microscope and determine whether it is unequivocally a malignant tumoror normal hematoma.
Sometimes it happens that a histological examination disproves the patient's nail melanoma and diagnoses other diseases: subungual hematoma, usually due to bleeding or bruising, fungal infection, purulent granuloma, paronychia, squamous cell carcinoma. If a malignant tumor is found in the histological examination, the ultrasound examination( ultrasound) of organs and the tomography are the final step to exclude the presence of metastases. How long does subungual melanoma develop? About this below. 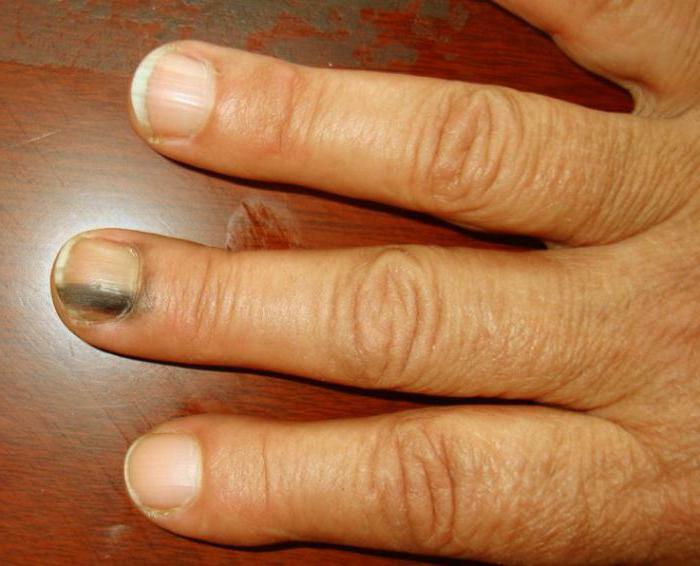
Treatment of
nail melanoma with Melanoma together with part of healthy tissues, as well as subcutaneous fat and muscle is completely removed( excised) surgically. Sometimes it happens that melanoma has already spread. Then, together with her completely remove the nail plate, and in especially neglected cases, the whole phalanx of the finger of the hand or leg is amputated. Also, if a patient is diagnosed with a nail melanoma, he is prescribed a lymphatic tissue biopsy, which will help doctors determine the extent of the spread of the malignant tumor to the local lymph nodes. Subungual melanoma of the thumb is common.
If, as a result of a histological examination, metastases are detected, then they are further removed. In addition, complete removal of lymph nodes is prescribed, and further, depending on the individual characteristics of the patient's body, complex or combined treatment is prescribed.
Additional methods of
Additional methods to combat this disease are: 
- Chemotherapy.
- Radiation therapy.
- Laser Therapy.
If the nail plate did not remove anything, then after the operation to remove melanoma the nail again grows.
Forecast
If the patient in a medical institution was provided with timely and competent help, then the forecast for him will be very favorable.
If the patient does not bother to apply to a qualified specialist on time, the visit was prolonged for a long period, then the tumor can already give metastases and the treatment process in this case is greatly complicated, because the chances of survival are decreasing. Approximately 15 to 87% of patients survive the diagnosis after five years.
Therefore appreciate your health, do not neglect it and at the first symptoms immediately consult a doctor.
