Anticholinergic drugs: list. The mechanism of action of the anticholinergic drug
Anticholinergic drugs are medicinal substances that block the action of the natural mediator - acetylcholine - on the cholinergic receptors. In the foreign literature this group of medicinal substances is called "deliriants" due to the ability to cause delirium. 
A few historical facts
Earlier, in the mid-20th century, anticholinergic drugs were used to treat chronic obstructive pulmonary and bronchial asthma, but they were replaced by more modern drugs with fewer side effects. With the development of pharmacology, scientists were able to develop such holinoblokatory, which do not have the same huge list of side effects. Dosage forms have been improved, and in the therapeutic practice of pulmonary diseases anticholinergic drugs have again been used. The mechanism of action of this group of drugs is quite complex, but it is possible to describe the main links.
How do holinoblokatory?
The main effect of the anticholinergic drug is to block the cholinergic receptors and the impossibility of affecting them with a mediator - acetylcholine. For example, in the bronchi, receptors located in the smooth muscles are blocked.
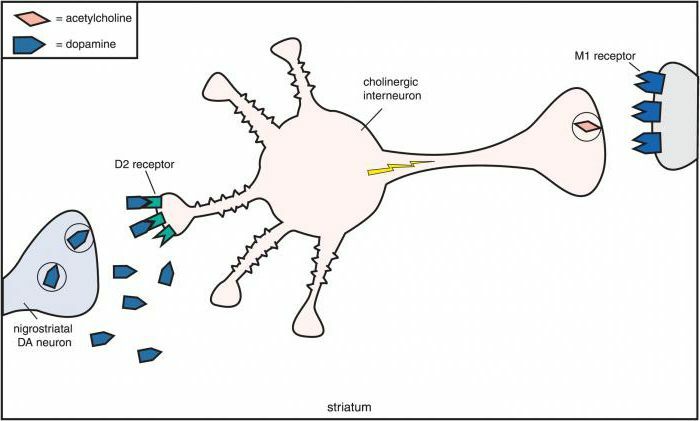
Classification of
preparations Depending on which receptors are affected by anticholinergic drugs, the list is divided into large groups:
- M-holinoblockers( atropine, scopolamine, ipratropium bromide).
- N-holinoblokatory( pentamine, tubocurarine).
Depending on the selectivity of the action:
- Central, or non-selective( atropine, pyrensepine, platyphylline).
- Peripheral, or selective( ipratropium bromide).
M-holinoblokatory
The main representative of this group of drugs is atropine. Atropine is an alkaloid that is found in some plants, such as belladonna, whitened and dope. The most pronounced property of atropine is spasmolytic. Against the background of its action, the muscle tone of the digestive tract, bladder, and bronchi decreases.
Atropine is administered by mouth, subcutaneously and intravenously. The duration of its action is about 6 hours, and when using atropine as drops, the duration increases to seven days.
Pharmacological effects of atropine:
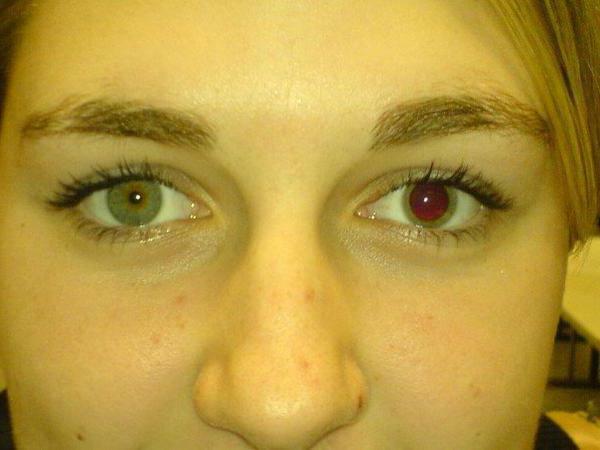
- The dilatation of the pupils of the eyes due to the stimulating effect on the circular muscle of the iris - the muscles of the iris relax, respectively, the pupil expands. The maximum effect occurs 30-40 minutes after instillation.
- Paralysis of accommodation - the lens is stretched and flattened, anticholinergic medications tune the eye to a distant vision.
- Heart rate contraction
- Relaxation of smooth muscles in the bronchi, gastrointestinal tract, bladder.
- Decreased secretion of internal glands, such as bronchial, digestive and sweaty.
Application of atropine
- In ophthalmology: examination of the fundus, determination of the refraction of the eye.
- In cardiology, atropine is used for bradycardia.
- Pulmonology uses anticholinergic drugs for bronchial asthma.
- Gastroenterology: with peptic ulcer of stomach and duodenum, hyperacid gastritis( by reducing the secretion of hydrochloric acid by the digestive glands).The drug is effective in intestinal colic.
- In anesthesiologists, atropine is used in the form of premedication before various surgical interventions.
Side effects of atropine.
Dry mouth and throat, photophobia, short vision, constipation, difficulty urinating are common.
Atropine is categorically contraindicated in glaucoma due to the effect of increased intraocular pressure. Contraindicated anticholinergic drugs for urinary incontinence, because they relax the muscles of the bladder. Cholinolytics require an accurate selection of dosage. When the dose is exceeded, poisoning of the organism occurs, which is characterized by motor and emotional arousal, pupil dilatation, voice hoarseness, difficulty in swallowing, and possibly a fever. With more severe poisoning, patients begin to lose their orientation in space, they cease to recognize the surrounding people, hallucinations and delusions are manifested. It is possible to develop seizures that pass into a coma, and due to paralysis of the respiratory center, death quickly begins. The most sensitive to excess of the dose are children - their lethal dosage is 6-10 mg. 
Scopolamine is similar in structure to atropine, but unlike it, it exerts a predominantly depressing effect on the central nervous system, acting as a sedative. It is this property that is used in practical medicine - scopolamine is used for various disorders of the vestibular apparatus - dizziness, abnormality of gait and balance, to prevent the development of sea and air sickness.
Anticholinergic drugs are included in the drug "Aeron", which is often used before the upcoming trips on airplanes and ships. The action of the tablets lasts about 6 hours. There is a non-tabulated form - a transdermal therapeutic system - a patch that glues behind the ear and secrete the drug for 72 hours. These anticholinergic drugs - antidepressants, in especially neglected cases help to quickly raise the mood of a patient who is in chronic depression.
Ipratropium bromide( Atrovent) is a bronchodilator. When inhaled, it is practically not absorbed into the blood and does not have a systemic effect. Due to the blockade of the cholinergic receptors of the smooth musculature of the bronchi, they expand. These anticholinergic drugs are available in the form of a solution for an inhaler or a metered aerosol, and are effective in bronchial asthma and COPD.Side effects - nausea and dry mouth.
Tiotropium bromides are anticholinergic drugs, similar in properties to ipratropium bromide. Produced in the form of powder for inhalation. A distinctive feature of this drug is that it lasts longer on cholinergic receptors, therefore it is more effective than ipratropium bromide. It is used in COPD.
Platyphylline is the alkaloid of the cross. Unlike other holinoblokatorov, platifillin is able to dilate blood vessels. Due to this property, a slight decrease in blood pressure occurs. The drug is released as a solution and rectal suppositories. Applied with spasms in the smooth muscles of the internal organs, liver and kidney colic, bronchial asthma, as well as with pain caused by spasm in exacerbation of peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum. In ophthalmic practice, platyphylline is used in the form of eye drops to dilate the pupils.
Pyrenzepine - predominantly blocks gastric cells that release histamine. By decreasing the secretion of histamine, the release of hydrochloric acid decreases. In conventional therapeutic doses, this drug has almost no effect on the pupils and heartbeat, so basically pirenzepin is taken internally for the treatment of peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum. 
N-holinoblokatory( ganglioblokatory)
The mechanism of action is that anticholinergic drugs of this group block sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation at the level of nerve nodes, reduce the release of adrenaline and noradrenaline, inhibit the excitation of the respiratory and vasomotor center. Moreover, the greater the influence of sympathetic or parasympathetic innervation, the greater the blocking effect.
For example, the size of the pupils is more strongly influenced by parasympathetic innervation - as a rule, the pupils are usually narrowed. In this case holinoblokatory will affect the parasympathetic nervous system - as a result, the pupils will expand. Virtually all blood vessels are under the influence of the sympathetic nervous system - drugs eliminate its influence and dilate the blood vessels, which reduces the pressure.
N-holinoblokatory have a bronchodilating effect and are used for bronchospasm, reduce the tone of the bladder, so these anticholinergic drugs can be prescribed with difficulty urinating. In addition, these medicinal substances reduce the secretion of the internal glands, as well as slow the peristalsis of the gastrointestinal tract. In medical practice, the hypotensive effect, which these anticholinergic drugs possesses, is used. The list of side effects is extensive:
- From the digestive tract: dry mouth and constipation.
- On the part of the respiratory system: cough, there may be a feeling of local irritation.
- From the CCC side: arrhythmias, marked palpitation. These symptoms are rare and easily eliminated.
- Other effects: possible reduction of visual acuity, development of acute form of glaucoma, edema.
Contraindications to the use of anticholinergic drugs
- Hypersensitivity to derivatives of atropine and other components of drugs.
- Pregnancy( especially the first trimester).
- Lactation.
- Child age( relative contraindication).
- Absolutely contraindicated the use of drugs in closed-angle glaucoma, in patients with renal insufficiency, it is necessary to carefully monitor the blood and urine.


