The glandular tissue and its structure
As you know, the whole human body is made up of cellular structures. They, in turn, form tissues. Despite the fact that the structure of cells is almost the same, there are differences in appearance and functions between them. At a microscopy of a site of an organ it is possible to estimate, from what tissue this biopsy is composed, and whether there is any pathology. Cellular composition plays a special role in the diagnosis of many pathological conditions. Among them - dystrophy, inflammation, tumor degeneration. Most of our organs are lined with epithelial tissue. With her help, the skin, the digestive tract and the respiratory system are formed.
Glandular tissue: structure
Histologists subdivide the body tissues into four varieties: epithelial, connective, muscular and nervous. Each of them forms a multitude of cells that are identical in structure. In a separate group can be attributed glandular tissue. In fact, it is formed from epithelial cells. Each of the tissue groups has its own structural features. Special medical science, histology, deals with the study of this issue.
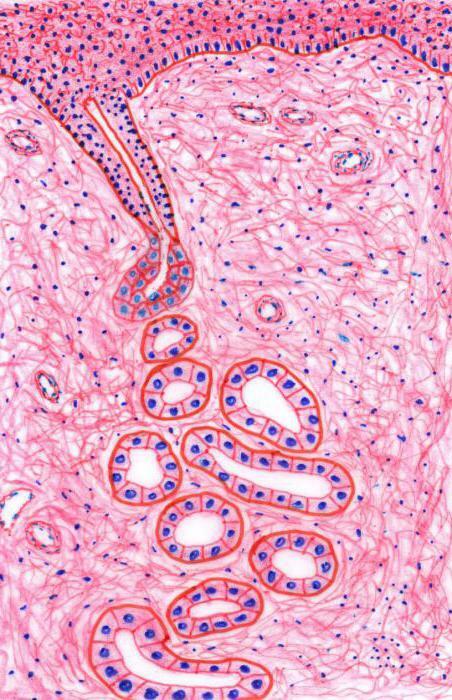
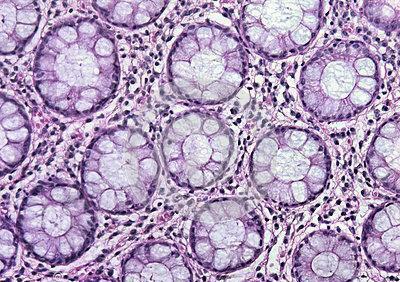 Epithelial tissue is characterized by a close arrangement of cells. There is practically no space between them. Therefore, it is quite strong. Due to the cohesion of cellular structures, the epithelium protects other tissues from damage and penetration of bacterial particles. Another cutaneous feature is rapid recovery. The cells of the epithelium are constantly divided, as a result of which it is constantly renewed. One of its varieties is glandular tissue. It is necessary for the secretion of secretions( special biological fluids).This tissue has an epithelial origin and lining the internal surface of the intestine, the airways, as well as pancreatic, salivary and sweat glands. Various pathological processes lead to a decrease or increase in the secretion.
Epithelial tissue is characterized by a close arrangement of cells. There is practically no space between them. Therefore, it is quite strong. Due to the cohesion of cellular structures, the epithelium protects other tissues from damage and penetration of bacterial particles. Another cutaneous feature is rapid recovery. The cells of the epithelium are constantly divided, as a result of which it is constantly renewed. One of its varieties is glandular tissue. It is necessary for the secretion of secretions( special biological fluids).This tissue has an epithelial origin and lining the internal surface of the intestine, the airways, as well as pancreatic, salivary and sweat glands. Various pathological processes lead to a decrease or increase in the secretion. Functions of glandular tissue
The glandular tissue is present in many organs. It forms both endo- and exocrine structures. Nevertheless, the organs can not consist only of glandular tissue. In any biopsy, several( at least 2) kinds of cells must be present. Most often, the body has both connective and glandular epithelial tissue. Its main function is to develop secrets. A large accumulation of glandular tissue is present in the breast in women. After all, this organ is necessary for lactation and feeding offspring.
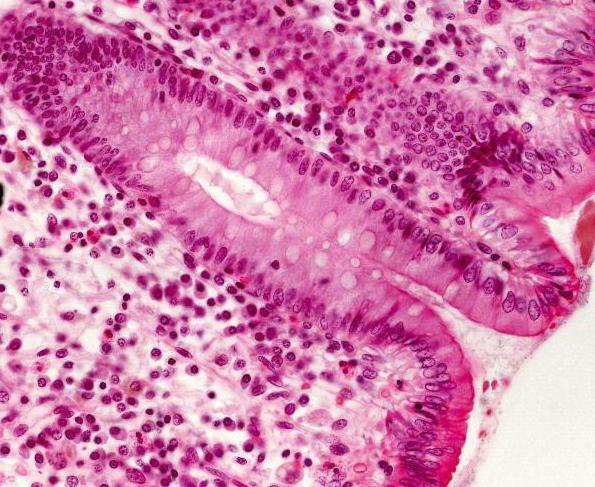
Breast milk is a secret that secretes glandular cells. During lactation, the tissue increases in volume by expanding the ducts. In addition to the breast, there are many organs that form glandular epithelium. The tissue of all endocrine formations produces hormones. They are biologically active substances, involved in many metabolic processes. Nevertheless, the endocrine glands do not produce a secret. This is their difference from exocrine organs.
Breast structure: histology
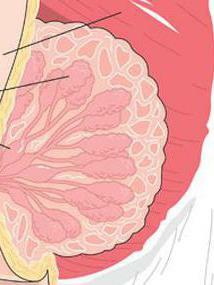
Glandular breast tissue is present not only in women, but also in men. Nevertheless, they have atrophied. The mammary gland is a paired exocrine organ. Its main functions are the formation and excretion of milk. In addition to glandular cells, the organ consists of connective and adipose tissue. The latter is on the periphery and protects the epithelium from damage. Also, due to fat tissue forms and size of the breast. The glandular tissue of the mammary glands is formed by cubic epithelial cells. It is in them that milk is produced during lactation.
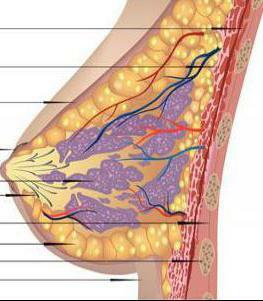
Almost in an equal proportion, in addition to the glandular epithelium, there is also connective tissue in the breast. It passes along the lobules and divides them among themselves. The violation of the relationship between these 2 types of tissue is called mastopathy. Slices, consisting of glandular tissue, are located on top of the pectoral muscle. They are present all around the organ's circumference. To separate the gland into lobular structures, connective tissue is necessary. It is also located on the entire circumference of the chest. As a result, the lobules gradually narrow and pass into the milk ducts( milky ways), which in turn form a nipple. It should be borne in mind that right under the skin there is fat tissue. It protects the gland from damage. This layer permeates the entire thickness of the body, as a result of which this part of the body has a definite shape. This explains the reduction in breast weight and, on the contrary, its increase after weight gain.
Why does the glandular tissue proliferate?
The proliferation of glandular epithelium occurs quite often. This especially applies to the mammary glands. The increase in tissue volume is caused by various metabolic disorders. After all, the mammary gland is an organ whose work depends on hormonal regulation. The proliferation of breast tissue leads to various diseases.
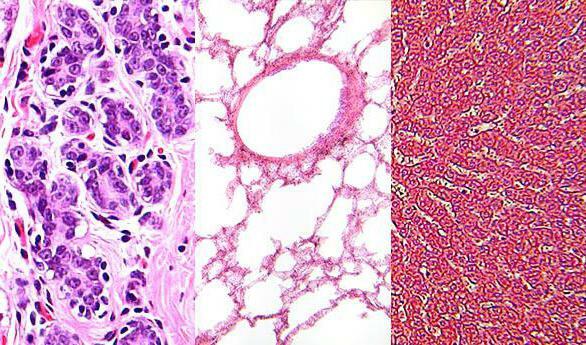
The following causes of hyperplasia of glandular tissue are distinguished:
- Gynecological pathologies. Especially it concerns chronic inflammatory diseases of appendages. Adnexitis is one of the main causes of the development of mastopathy in women.
- Admission of hormonal drugs. In recent years, the main method of contraception is the use of COCs. This method is really effective. Nevertheless, when taking oral contraceptives for a long time, it is necessary to consult a mammologist.
- Thyroid gland diseases. It should be noted that the decrease in the hormonal activity of this organ( hypothyroidism) is observed in the majority of women suffering from cystic mastopathy.
- Stressful situations.
- Hormonal disorders. Most often they develop after abortions, with multiple pregnancies or, on the contrary, their absence.
- Pathologies of the pituitary and adrenal glands.
Pathologies of glandular tissue: classification of
In some diseases, glandular tissue in the breast begins to grow rapidly. This leads to the fact that the epithelial cells begin to predominate over the fibrous structures. As a result, the tissue ratio in the mammary gland is disrupted. Thus, the development of breast disease. The following pathologies of the breast are distinguished:
- Mastopathy. This disease can have both local( localized) and diffuse( widespread) nature. The second variant of pathology is most often observed. Depending on the tissue ratio, cystic, fibrotic and mixed mastopathies are isolated.
- Fibroidadenoma of the breast is most common in young girls. This disease is characterized by the appearance of a benign neoplasm consisting of fibrous tissue and surrounded by a capsule.
- Intra-flow papilloma. It is an overgrowth of epithelial tissue. The main symptom of this pathology is the appearance of blood from the nipple.
- Breast cancer.
Fibrous-cystic mastopathy
If the glandular fibrous tissue is present in a normal ratio, this indicates that there is no breast pathology. Sometimes the elements of the epithelium predominate. If the glandular tissue is larger than fibrous tissue, then such a pathology as cystic mastopathy is observed. Another name for this disease is adenosis. With glandular hyperplasia, the lobes and ducts widen, small cavities - cysts are formed. Change in tissue structure can be suspected during palpation of the breast. A careful examination reveals the granularity of the mammary gland. There may be several small cysts.
Fibrous mastopathy is characterized by the fact that the connective tissue predominates in the structure of the organ. When palpation, a lot of dense knots( strands) are found on the entire surface of the breast. Most often there is a combined hyperplasia of both connective and glandular tissue. In this case, the disease is called fibrocystic mastopathy. This pathology is widespread among women of all ages.
Localized lesions of glandular tissue
Localized non-tumorous breasts, like diffuse, can be formed from fibrous and glandular tissue. Unlike common processes, they are clearly delineated in the tissues of the organ. The most common disease in this group is the cyst. It is formed as follows: the glandular tissue of which the lobule is composed, stretches and grows in size, resulting in a cavity with a cloudy or transparent content - a cyst that has a rounded shape and a soft consistency. When the palm is pressed down on the chest, the cyst is not detected( König's symptom is negative).
Another localized pathology is fibroadenoma. Unlike cysts, it is dense on palpation and very mobile in the gland tissue. If you press the chest with your palm, fibroadenoma does not disappear( a positive König symptom).
Diagnosis of pathologies of glandular tissue
Disease of glandular tissue must be differentiated from other non-tumor pathologies of the breast( fibrotic mastopathy) and cancer. For this, palpation of the organs is performed. Thanks to a thorough feeling of the chest, you can find out what shape, size and consistency is formed. In addition, ultrasound of the breast and mammography is performed. With the help of these studies, it is possible to determine such pathologies as mastopathy and breast cyst. Cytological and histological analyzes are performed for the diagnosis of breast cancer. To study the cellular composition of the contents of the cysts, a puncture biopsy is necessary.
How to stop the increased proliferation of glandular epithelium?
To stop the pathological growth of glandular tissue, phytotherapy and medical treatment are recommended. Herbs that are used for fibrocystic mastopathy, it is necessary to brew and drink in the complex. Among them: sage, red brush, oregano, hemlock, burdock, nettle and meadow chamber. Drugs called "Mastodinon" and "Progestogel" are referred to as medicines.
Prophylaxis of glandular tissue hyperplasia
To avoid hyperplasia of the glandular tissue, it is necessary to treat gynecological inflammatory diseases in time and to be examined by a specialist at least 2 times a year. Women after 40-50 years are recommended to perform mammograms. In addition, it is important and independent examination of the mammary glands. It is carried out in the first days after menstruation.
Complications of diseases of glandular tissue
It is worth remembering that pathologies such as fibrous and cystic mastopathy are background diseases for breast cancer. It can be formed from both immature glandular and connective tissue. Therefore, if there are any seals or tenderness in the chest, immediately see a doctor.
