Cervical lymphadenitis( ICD 10 - L04): types and methods of treatment
Cervical lymphadenitis( ICD 10 - L04) is an inflammation of the lymph nodes in a chronic or acute form. Cervical localization almost immediately manifests itself in the form of typical symptoms, which makes it possible for a timely start of therapy and, accordingly, a quick recovery.
Most often, cervical lymphadenitis occurs against a background of oral disease, which can be caused by infection with microorganisms, viruses or bacteria. A distant purulent focus can also become a prerequisite for lymphadenitis. 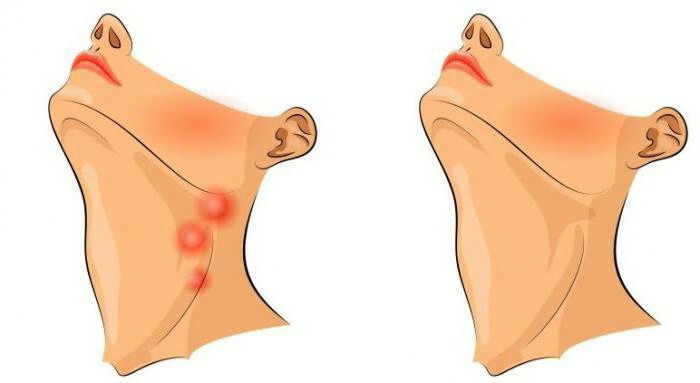
Causes of lymphadenitis
Quite often inflammation of the lymph nodes is preceded by the process of suppuration in the face area. Staphylococci and streptococci are the most common pathogens. Depending on the cause of the onset, lymphadenitis is divided into specific and non-specific.
The cause of specific lymphadenitis can be severe infectious diseases, such as diphtheria, tuberculosis and others. Nonspecific form of the disease occurs due to direct infection in the lymph node. It can happen through a wound on the neck.
The risk group for cervical lymphadenitis( ICD 10 - L04) includes patients with weakened immune system, children, working with animals, land and dirty water, who are often infected with infectious diseases. Most cases occur in patients older than 18 years.
Aggravating factors
 There are several factors that cause the risk of the disease:
There are several factors that cause the risk of the disease:
- infectious disease of the nasopharynx and oral cavity;
- disorders of the endocrine system, including the thyroid gland;
- human immunodeficiency virus;
- allergic reaction with complications;
- pathology of the metabolic process;
- excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages.
Cervical lymphadenitis( ICD 10 - L04) is not contagious, it is a secondary process that occurs as a complication of a viral or bacterial infection. Depending on the concomitant diseases, lymphadenitis therapy is performed by an otolaryngologist, infectious disease specialist, surgeon, etc.
At the initial stage, lymphadenitis manifests itself in an acute form, gradually turning into a chronic stage. Sometimes the symptoms do not appear in the introductory stage. It depends on the state of the patient's immunity.
Types of
Types of cervical lymphadenitis( ICD 10 - L04) are presented below: 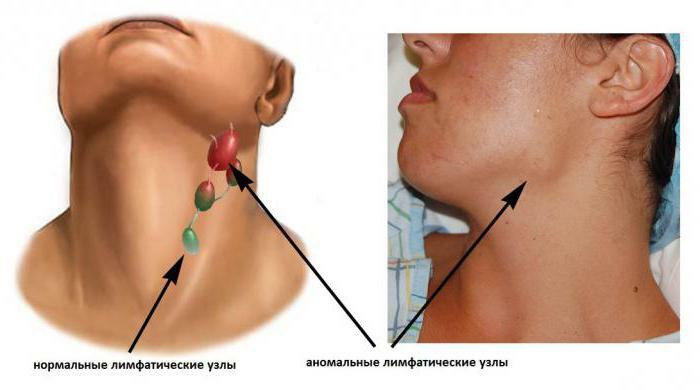
- nonspecific inflammation of occurs when a fungus or virus infection enters the lymph node, is easier to treat, less likely to lead to complications;
- specific inflammation of is a sign of severe pathology, including tuberculosis, syphilis, typhoid and plague
In this case, the diagnosis is already in the stage of chronic course. There are several stages of the disease in acute form:
- Serous .Does not cause intoxication and severe fever. The initial stage of penetration of a harmful microorganism into the lymph node.
- Purulent .Indicates infection with bacteria. It is accompanied by a high temperature and requires surgical intervention.
- Complicated with .It requires urgent surgical intervention, as it can lead to infection of the whole organism.
The course of the nonspecific form of cervical lymphadenitis( ICD code 10 - L04) is characterized by the spread of the virus through the lymph node and fungi. This form is well amenable to therapy and rarely causes complications. The spread of the disease to other lymph nodes can lead to the development of severe pathology called generalized lymphadenitis. 
Symptoms of cervical lymphadenitis
Common symptoms indicative of lymphadenitis are:
- temperature increase in the acute stage of the disease;
- sleep disturbances, loss of appetite, weakness;
- Neurological disorders, apathy, dizziness, migraines;
- intoxication.
At the onset of acute cervical lymphadenitis( ICD code 10 - L04), lymph nodes enlarge and enlarge. Palpation is painful. This is considered serous and requires a doctor. Otherwise, the disease will progress and go into a chronic form.
 Symptoms characterizing the chronic form of lymphadenitis are:
Symptoms characterizing the chronic form of lymphadenitis are:
- swelling of the lymph nodes;
- increased body temperature;
- drowsiness, general malaise, sleep disturbance;
- slight soreness on palpation.
At the stage of chronic lymphadenitis of the cervical lymph nodes( ICD 10 - L04), symptoms become unexpressed. This is due to the fact that the body reduces the amount of resources that are spent on fighting the disease and get used to the existing condition. As a result, the organism is intoxicated with the products of decay and the areas that have undergone necrosis.
Purulent tissue damage leads to an increase in the external manifestations of the disease and, as a result, is rapidly exacerbated. The purulent stage will be indicated by pulsation and severe pain, as well as a strong swelling of the lymph nodes. This condition is considered life threatening and requires immediate intervention.
Diagnostic methods
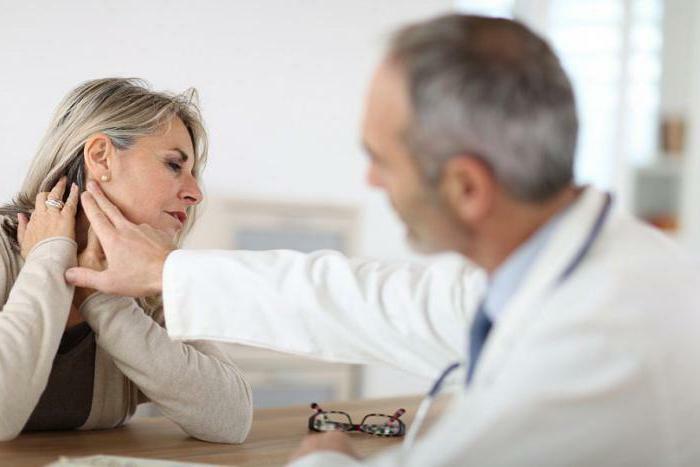
How is cervical lymphadenitis identified( ICD 10 - L04)?During the examination, the specialist palpates the affected lymph nodes, as well as the surrounding tissues to determine the cause of the disease. A general blood test will provide information on the presence of an inflammatory process, accompanied by an increase in the number of lymphocytes. 
If lymphadenitis is diagnosed without concomitant complications, immediate treatment is required. In case the doctor observes changes in other organs and systems, an additional examination is required, including such tests:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- a study on the histology of the lymph node material via puncture;
- X-ray examination of the chest( performed with suspicion of tuberculosis);
- of the abdominal ultrasound if the cause of the inflammatory process has not been established;
- blood test for the immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis.
Regardless of the stage of the disease, a visit to the doctor is strictly mandatory. Exacerbation of lymphadenitis can occur at any time.
Treatment of
Purulent cervical lymphadenitis( ICD 10 - L04) is treated exclusively surgically. The focus is opened, the contents are removed, the wound is treated and drained. After this, symptomatic therapy is performed. Conservative treatment is carried out depending on the factor that caused the disease. Most often, analgesics, restorative drugs and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. In the period of remission, physiotherapy is allowed.
Preventative measures
With regard to prevention, it is necessary to immediately treat purulent and inflammatory diseases that arise in the chest and face. Since the disease can occur against the background of infection of the oral cavity, you should regularly visit the dentist for preventive purposes.
In addition, prevention of lymphadenitis involves the intake of vitamin-mineral complexes, the timely processing of scratches and wounds on the skin, as well as the treatment of abscesses, boils, etc. Treat lymphadenitis at home is unacceptable. Inflamed lymph nodes can not be heated or applied to them compresses!
