Minimally invasive surgery: clinics and centers
Medical technology does not stand still;their development significantly expands the possibilities - both diagnostic and therapeutic stage.
In particular, due to the active development of the endoscopic technique, minimally invasive surgery has become quite widespread. Consider what it is, in this article.
Why Minimally Invasive Surgery
All the subtleties of this technique are aimed at minimizing the traumatic effects on the patient's body, which are inevitable in any surgical intervention.
Examples of techniques include endoscopy and laparoscopic surgery.
The combination of laparoscopy with alternative ways of access to internal organs can also be attributed to minimally invasive surgery.
The popularity of the method is easy to explain.
This technique is suitable both for patients' interests( the consequences of these operations are minimal) and for socioeconomic interests( thanks to the use of minimally invasive surgery, it is possible to significantly shorten the period of the patient's stay in the hospital.)
Laparoscopy has found wide application in pediatric abdominal surgery:on the organs of the abdominal cavity is carried out with the help of laparotomy. Laparoscopic operations are possible in children of almost any age.a set of instruments for laparoscopy with different diameters are available for working with small patients of different ages
In pregnant women, the possibility of carrying out laparoscopic operations is very limited
![], endoscopic minimally invasive surgery](/f/de/8b/de8b0a4ae2f0dea6fda68d8d0a7cc40b.jpg)
Advantages of
- The damage to the patient's body during surgical intervention performed in accordance with minimally invasive surgical techniques is significantly lower, than at usual operative access.
- In the long bed mode after a minimally invasive operation it is not necessary. Such manipulations can be carried out in special clinics of minimally invasive surgery( so-called clinics of one day).
- Low-trauma surgery is well tolerated by patients.
- The level of traumatization of body tissues under such manipulations is significantly lower because of the reduction in the time of intervention;and a low level of trauma can increase the therapeutic and cosmetic effects.
Examples from the history: how it all started
The very first laparcopic operation was carried out in France in the 80s of the 20th century. Several years later, this method has already been introduced into mass application.
After the beginning of systematic use of this technique has received rapid development and for quite a short time has become very popular.
Minuses of low-impact interventions
- Operative interventions performed with the help of endoscopic techniques do not allow palpation of tissues.
- The need to install high-tech equipment in a medical institution or the establishment of special centers for minimally invasive surgery;high cost of such equipment.
- Necessity of getting medical staff skills in working with high-tech equipment.
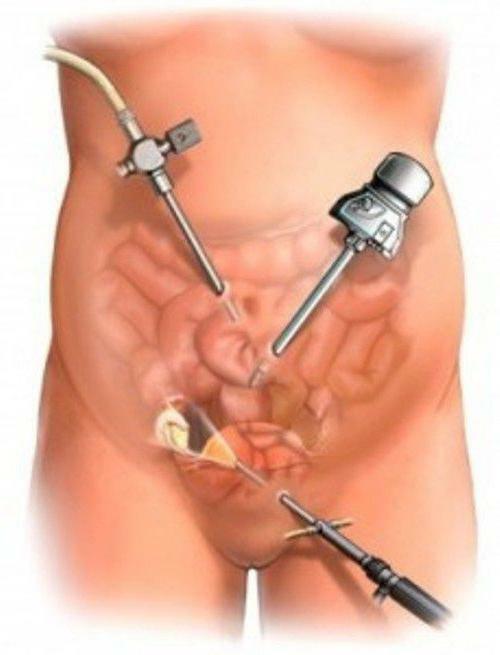
Laparoscopy
This type of minimally invasive surgery can be used in the following situations: ![], clinic of endoscopic and minimally invasive surgery](/f/55/ad/55ada5e19e101497a8833b8ac3245180.jpg)
- Female infertility.
- Treatment of endometriosis.
- Ovarian cysts.
- Uterine fibroids. Ectopic pregnancy.
- Removal of the gallbladder.
- Removal of small size of neoplasms of internal organs.
- Removal of lymph nodes.
- Treatment of certain vascular pathologies.
Operative intervention begins with the fact that in the anterior abdominal wall produce three or four punctures. Subsequently, through them, carbon dioxide is introduced into the body, which is necessary to increase the volume of the cavity and create sufficient space for the operation. Then, through one of the punctures, a camera is inserted, which displays on the monitor the operating field, internal organs and instruments introduced to perform manipulations through the remaining punctures.
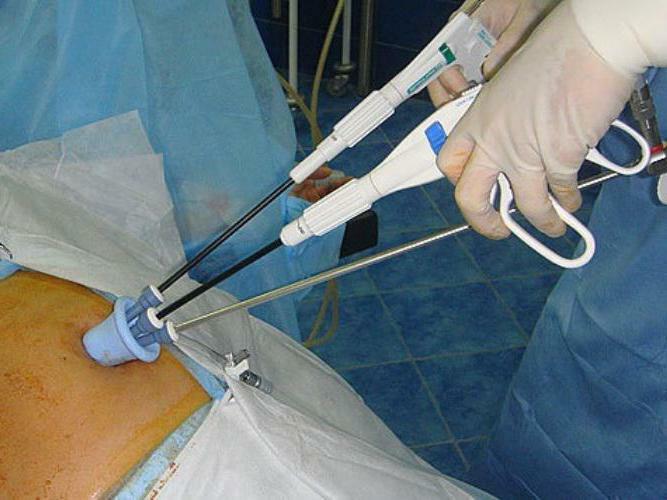
Mini-laparotomy( mini-access)
In essence, in this case, a normal surgical operation is performed, but through a much smaller incision, which is made possible by the use of a special set of instruments. In this way, many surgical interventions on the abdominal organs can be performed.
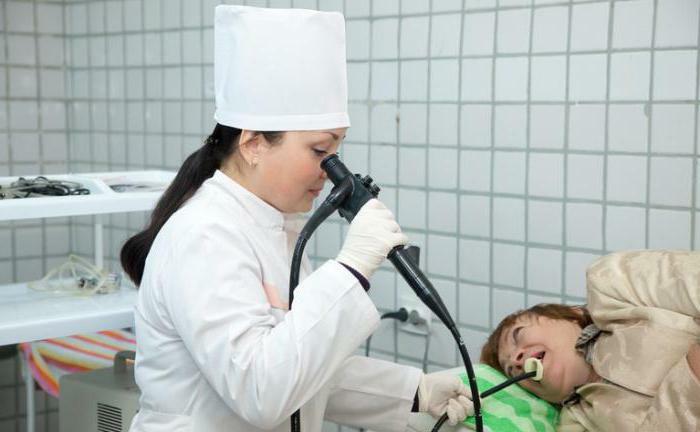
Endoscopy
This technique is used for examination of internal organs having a hollow structure and is carried out with the help of special tools - endoscopes.
Endoscopic minimally invasive surgery, unlike laparoscopy, does not use punctures or incisions;Medical instruments are inserted into hollow organs through natural openings. Accordingly, recovery after such manipulation is much easier.
Thus, in the clinics of endoscopic and minimally invasive surgery and endoscopic departments of hospital complexes, the following organs are examined:
- esophagus;
- stomach;
- intestine;
- larynx;
- trachea;
- bronchi;
- urinary bladder.
In addition to the examination, endoscopy also provides opportunities for medical procedures, for example, stopping gastric bleeding, removing a small size of stomach and intestinal tumors. Such manipulations are carried out both in usual medical institutions, and in specialized clinics( for example, clinic of coloproctology and minimally invasive surgery).

Rehabilitation period
Due to the low level of traumatization of tissues and organs in operations performed in accordance with the principles of minimally invasive surgery, the rehabilitation period after such interventions has a minimal duration and is well tolerated by patients.
In the appointment of prolonged bed rest with the use of low-traumatic methods of surgery is not necessary.
Pain syndrome in small operations is significantly less, this circumstance makes it possible to avoid the use of drugs belonging to the group of analgesics, and consequently, their side effects.
When minimally invasive surgery is not suitable
Despite all the advantages, minimally invasive surgery can not be used in all cases. Some surgical interventions can not be transferred to the category of low-traumatic ones.
- The presence of adhesive process in the abdominal cavity. This circumstance is an obstacle for some of these operations. Particularly serious problems are cases when the patient has a history of several surgical interventions that led to the formation of adhesions. However, in some cases, when the patient is refused laparoscopic surgery on the abdominal organs due to the presence of adhesions, surgical intervention can be made from the so-called mini-access. A single-valued algorithm does not exist;the decision is made in each case individually.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system and lungs in the stage of decompensation. This is due to the fact that for laparoscopy requires the introduction of abdominal cavity carbon dioxide;and this, in turn, will lead to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure and the creation of additional pressure on the diaphragm and, as a consequence, on the organs of the thoracic cavity. In patients with cardiopulmonary failure, such an effect leads to a worsening of the condition.
- Sharply increased weight of the patient. Obesity of the third and fourth degree can also be a contraindication for carrying out laparoscopic surgery due to the fact that access to internal organs in these cases may not be enough for the length of the instruments. In addition, due to the high mass of the anterior abdominal wall, in such cases, in some cases, it is not possible to create a pneumoperitoneum.
- Ophthalmic hypertension, in particular, with glaucoma. Pneumoperitoneum can provoke an increase in intraocular pressure, worsening of the course of this severe disease and the development of complications( for example, retinal detachment).
- High degree of myopia - above six diopters( for the same reasons - to avoid detachment of the retina).However, in some cases, exceptions are possible, for example in the case of a short-term exposure or a malologic laparoscopy, when intra-abdominal pressure rises slightly.
- Diseases of the blood system, characterized by a violation of its ability to clot. Such conditions are fraught with increased bleeding, which is unacceptable.
In the elderly, a whole complex of circumstances, which are contraindications to laparoscopic surgical intervention, is often recorded. In such cases, patients undergo an operation using the mini-access technique, which has virtually no common contraindications.
