Divisions of the small intestine: description, structure and functions
How do the thin and thick intestines interact with each other? What are the features of the work of the presented parts of the digestive tract? What role does the small intestine play in the absorption of nutrients? We will try to answer these and other questions in the material presented.
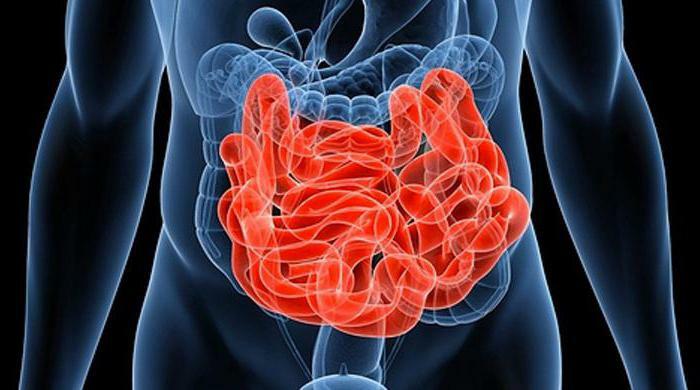
Divisions of the small intestine of a person
There are such sections of the small intestine:
- The duodenum connects with the inverted zone of the stomach. This initial section of the small intestine forms a horseshoe-shaped loop around the pancreas. The duodenum is almost completely located in the retroperitoneal cavity. Outside the boundaries of this space is only its small process - ampoule.
- The jejunum forms the upper part of the small intestine. Presented in the form of seven loops that lie in the left part of the peritoneum.
- The ileum is located in the lower right region of the abdominal cavity. Its end in the form of loops goes into the pelvic area. The ileum connects to the rectus and is in close proximity to the bladder, the uterus( in women).
Physical parameters of
The above sections of the small intestine in different areas have an uneven diameter. In the distal zone the indicator is 2-3 cm, in the proximal zone - 4-6.The thickness of the walls of the small intestine is 2-3 mm, and in the case of tissue contraction it reaches 4-5.The length of the small intestine as a whole can be 5-6 meters. Her weight in an adult is close to 650 g.
Small intestine: departments, functions
The most important processes of digestion occur precisely in the small intestine. The mucous membrane of local tissues produces a huge number of active enzymes. They process hummus - food mush, created by gastric juices. Here, useful elements are absorbed into the lymph and blood capillaries, which ensure their transportation to the tissues of organs and systems. Consider what functions are performed by the small intestine:
- Duodenum - hydrolysis of proteins, carbohydrates, fats. It ensures the active production of digestive enzymes. Produces processing of undigested food particles with bile, transportation of stomach contents.
- The jejunum - motor, suction, hormonal function, hydrolysis of polymers.
- The iliac zone is a transport-motor function. Provides absorption of substances that are formed as a result of hydrolysis. Recycles bile acids.

The ability of small intestine cells to produce hormones
The production of hormones is a special function of local tissues. The departments of the small intestine are not only part of the digestive tract, but are also part of the endocrine system. Here, a wide list of hormones that regulate the transport-motor and digestive activity of the intestine is produced.
The following set of endocrine cells is concentrated in the small intestine:
- I-cells - produce cholecystokinin;
- D-cells are somatostatin;
- M-cells - motilin;
- G-cells - gastrin;
- K-cells - insulinotropic glucose-dependent polypeptide;
- S-cells are secretin.
The bulk of the hormone-producing cells are located in the jejunum and duodenum. A small part of them - in the field.
How does digestion occur in the small intestine?
Digestion in the small intestine is performed as follows. Pre-treated with saliva and gastric juice, gruel, coming from the stomach, has an acid reaction. In the small intestine, the presented mass is exposed to alkaline action. Thus, optimal conditions are created for the processing of nutrients by enzymes. The cleavage of the protein components of the food pulp occurs under the influence of the following elements of intestinal juices:
- Enzymes of enterokinase, kinazogen, trypsin process simple proteins.
- Erepsin cleaves peptides into amino acids.
- Nuclease separates into microelements complex molecules of protein origin, known as nucleoproteins.
- Maltase, phosphatase, amylase and lactase enzymes break down carbohydrates.
- Lipase processes fats.
After the synthesis of nutrients from food pulp by enzymatic treatment, the carbohydrate and protein components are absorbed by villi in the small intestine. Further, the microelements enter the venous capillaries in the liver tissue. In turn, fats are sent to the lymphatic system.
Diseases of the small intestine
The most common ailments that affect the small intestine are diarrhea and stool retention in the pathways. Disorders of defecation are often accompanied by the development of pain syndromes in the peritoneum. Quite often, with poisoning and disorders of the small intestine, abundant gas formation is observed. However, the pain is of a short, moderate nature and is not the main factor of discomfort.
A common symptom of the development of disruptions in the operation of the small intestine is a rumbling in the peritoneum, a feeling of atypical movement in the abdomen. Most often, such manifestations are the result of abundant gas production as a result of consumption of legumes, cabbage, potatoes, rye bread. Significantly increase these symptoms can occur at night.
More serious consequences are caused by failures in the production of enzymes and the breakdown of food gruel into microelements. If the assimilation of food, due to the absorption of substances into the blood and lymphatic vessels, does not occur properly, it can lead to weight loss, weakening of bone and muscle tissue. The consequences of digestive disorders are often hair loss, dry skin, the appearance of swelling in the extremities.
There are several basic conditions that lead to the development of pathologies in the small intestine:
- Malabsorption - a violation of absorption of nutrients.
- Maldigestia - low digestive activity.
If to speak about insufficiently qualitative processing of a food slurry, similar phenomena arise against a background of low contents of enzymes in intestinal juices. Low fermentation can be either acquired or genetic. Usually pathologies of this plan are a consequence of chronic inflammations, endocrine diseases, surgical interventions.
Diagnosis
To diagnose the development of diseases of the small intestine, specialists resort to such methods of research:
- capsule examination;
- SPL;
- colonoscopy;
- endoscopy;
- fibroscopy;
- radiography.
As for the analyzes, standard procedures are provided here. The patient gives a sample of feces, blood is taken. Exercises are examined for the presence of helminths. When studying blood, the rate of movement of erythrocytes is taken into account. In addition, the diagnosis is performed, which makes it possible to evaluate the performance of the liver and thyroid gland.
Treatment of
Therapy, aimed at restoring the functions of the small intestine, involves, first of all, the elimination of the underlying disease. With a lack of enzymes in intestinal juices, preparations containing synthetic substitutes are used. In case of weight loss, funds are prescribed for parenteral nutrition of tissues. In the latter, there are emulsions of fats, amino acids, protein hydrolysates, concentrated glucose.
If problems are caused by intestinal dysbiosis, prescribe antibiotics. The latter can provoke partial or complete destruction of useful flora. For this reason, after taking the therapy, the patient is prescribed the intake of "Bifikol", "Lactobacterin" or "Colibacterin" - biological preparations, which have a positive effect on the restoration of the intestinal biocenosis.
Quite often, patients who suffer from disorders in the operation of the small intestine are prescribed medication, which causes compaction of stool. These include drugs with a high content of calcium, bismuth. If the formation of liquid stool causes insufficient adhesion of fatty acids, to solve the problem resorted to the use of activated carbon. All of the above negative symptoms require a prior consultation with a doctor. To bring the small intestine back to normal, it is important to give up self-treatment, make timely diagnosis and resort to an adequate, developed by a specialist in therapy.
In conclusion
Here we are, what is the small intestine, the departments, the structure of the part of the digestive tract represented. As can be seen, local tissues take a direct part in the processing of food, its splitting into individual trace elements. The small intestine produces enzymes, vitamins, hormones, substances that contribute to enhancing the protective functions of the body. At the same time, the emergence of a deficit of beneficial bacteria that live on its walls, always leads to the development of pathological conditions.
