Vaccination against poliomyelitis: side effects. When are vaccinated against poliomyelitis?
Vaccination always causes parents a lot of questions, disputes and experiences. A vaccine against poliomyelitis, whose side effects can sometimes cause problems in a child, tops the list of the most needed vaccines in childhood. After all, this severe disease affects the motor neurons, causing paralysis and other dangerous changes in the body. 
What is polio
Polio is a spinal paralysis in a child. After the virus enters the body and reproduces it, the gray matter of the spinal cord is affected, resulting in paralysis of the muscles, the neurons of which are more influenced by the virus. To prevent this disease can only be vaccinated against poliomyelitis. When vaccinations are made, the child should not have any respiratory diseases and exacerbations of chronic diseases.
The disease can occur in an erased or latent form( without symptoms), so sometimes it is difficult to identify it. Most of the poliomyelitis is common among children aged 6 months to 5 years. At this age, the baby is very difficult to follow, so the risk of getting sick is greatly increased. And given that poliomyelitis is transmitted by airborne droplets, we conclude: they can get infected in the most unexpected place.
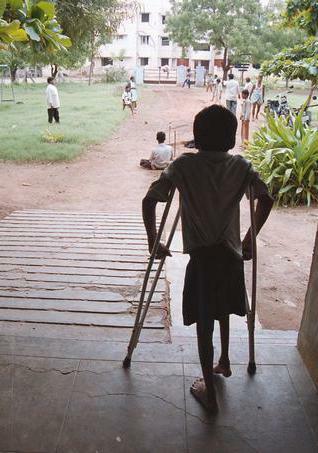
That's why polio vaccine is so necessary. There have always been many parents for and against vaccination. You can find out the positive and negative aspects of vaccination from this article.
The poliovirus is volatile and resistant to external influences. It can be stored in dairy products, water and stool for up to six months. That is why in the twentieth century this disease took the form of an epidemic.
The causative agent of the virus
The causative agent of poliomyelitis refers to the viruses of the family of picornaviruses and a group of enteroviruses( viruses that reproduce in the intestine).There are three independent strains. All these strains usually contain a polio vaccine. Side effects on the body will not harm the health of the child.
The virus is a single-stranded RNA encapsulated in a protein shell with inclusion of lipids. Not subject to the influence of environmental factors, resistant to freezing, but when boiled quickly dies. After entering the body, it multiplies in the tonsils, intestines and then affects the gray matter of the spinal cord, causing destruction of motor neurons and muscle tissue atrophy.
Symptoms of poliomyelitis
Time to determine the presence of the child's disease can be on the symptoms of the initial stage. Typically, this is:
- increase in body temperature;
- intestinal disorders;
- severe headaches;
- fast fatigue of the body;
- appearance of convulsive seizures.
If the child was not vaccinated, the first stage quickly passes into the second, and paralysis and paresis occur, localized in the muscles of the limbs and the deltoid muscle. Paralysis of muscles of the face, neck and trunk can occur less often. The vaccine against poliomyelitis will avoid possible contamination. Reviews about the used drugs can be studied in detail on the Internet. 
To protect your child from such a dangerous disease, it is better to vaccinate against all three viruses that cause poliomyelitis in advance. Otherwise, with paralysis of the muscles of the diaphragm, a lethal outcome is possible.
What is a vaccine against poliomyelitis
The vaccine implies the introduction into the body of a severely weakened or killed virus, resulting in the development of immunity to the disease. The multiplying virus will provoke the production of antibodies in the blood, and after a while it will be completely removed from the body, while the child will have so-called "passive" immunization.
The effect of vaccination against poliomyelitis depends directly on the site of its introduction. There are oral and inactivated forms of the vaccine. Oral vaccine drips directly into the baby's mouth, therefore it is more effective, but it can also give complications.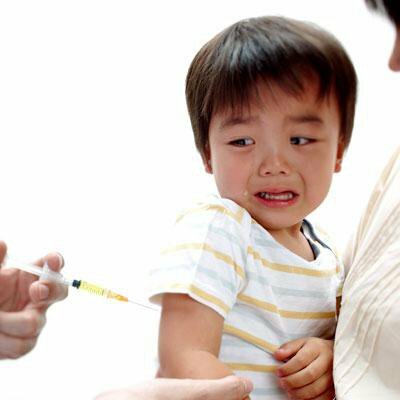 
As the natural virus multiplies in the digestive tract, the oral vaccine will promote the development of stronger immunity against poliomyelitis.
Inactivated vaccine is injected through the injection and is less dangerous for the child's body. Both drugs contain three known strains of the virus, so vaccination completely protects the child from the possibility of contracting polio.
When the vaccination is carried out
A certain system of children's vaccination is functioning in medical institutions:
- , the first introduction of inactivated vaccine( IPV) is carried out at 3 months;
- in 4,5 months - the second IPV is introduced;
- at 6 months is the third IPV;
- at 18 months, repeated revaccination with the introduction of oral vaccine( OPV);
- at 20 months - second revaccination of OPV;
- at the age of 14 is the last inoculation against poliomyelitis.
When all vaccines are made according to the schedule, the child develops a permanent lifelong immunity to the disease. In those cases when the schedule of vaccination was broken, it is necessary to take care of individual control and timely administration of the drug in order to protect your child from dangerous diseases. Carrying out the right vaccination will form a lifelong immunity in the child.
How many polio vaccinations need to be done can be obtained directly from the doctor, or by studying this issue with the help of specialized literature.
Where the polio vaccine is introduced
The introduction of the polio vaccine has its own characteristics. Live vaccine is administered orally - pink fluids should be dripped to babies on the lymphoid tissue of the pharynx, older children should be dripped with vaccines on the palatine tonsils. This is necessary to prevent excessive salivation, as getting the vaccine into the stomach neutralizes its effect( under the influence of gastric juice it breaks down).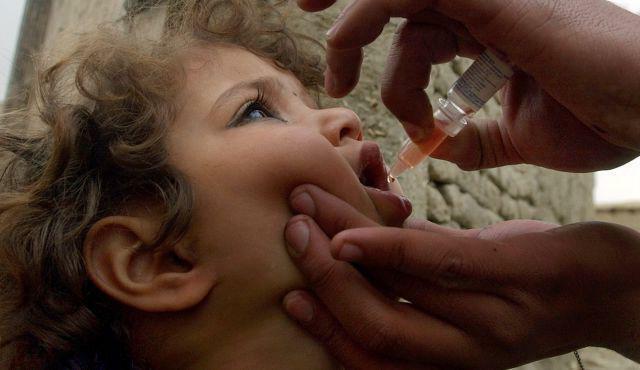
Please note! If the baby has a regurgitation, the procedure for administering the vaccine will need to be repeated.
The inactivated vaccine should be administered to children intramuscularly into the thigh area or subcutaneously into the scapula area. Older children are given the vaccine intramuscularly, in the shoulder area.
Vaccination against poliomyelitis: pros and cons of combination with the DPT vaccine
The DTP vaccine is used to protect a child from whooping cough, diphtheria and tetanus. In our medical institutions most often DTP and IPV do together. The vaccine can be administered by two different drugs, or in combination, with drugs such as Infarix Gesta and Pentaxim.
We should not worry that the combination of IPV with DTP will cause more complications than one vaccination against poliomyelitis. Side effects from this combination of drugs do not increase and are often completely absent.
Immunologists have been proven that the joint administration of vaccines promotes the development of a child's immunity at once to all diseases. However, it is better to consult a doctor individually on this issue, since DTP is severe for the body, and in some cases it is better not to combine these vaccines. When vaccinating a healthy child, there are no complications.
What drugs are used to vaccinate
To immunize a child, complex or monovalent drugs can be used. Among monovalent inactivated vaccines in our country are popular:
- "Polioriks" - produced in France. In its composition has all three strains of the virus, gently affects the child's body, causing the production of antibodies and the formation of stable immunity. Can be used for weakened infants, premature babies, underweight, and also combined with other vaccines.
- "Imovax polio" - is produced in Belgium. The drug is completely analogous to "Polioriks" both in composition and in the mechanism of action on the body.
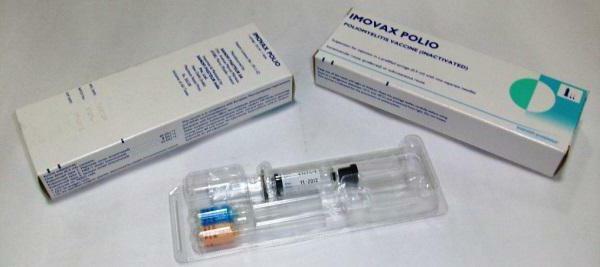
For a small child, the only guarantee against protection is a vaccine against poliomyelitis. Reviews of parents and doctors about her in the majority only positive. But what can I say, it can generally be called a vital procedure. And if the recommendations of the pediatrician are followed, the side effects will be minimal and safe for the baby's health.
For complex vaccines, the following are used:
- "Pentaxim" - produced in France. It is considered the best vaccine, as it is produced with a high degree of purification and protects against five diseases( CDS, hemophilia, poliomyelitis).
- "Tetrakok" - produced in France. It is a complex DTP vaccine with killed pertussis virus. The drug is safe for the child's body, since it does not contain a preservative-merthiolate in its composition.
- "Infanriks Gesta" - is produced in Belgium. It is an analogue of Pentaxim, the only difference is that pertussis in this vaccine is represented by only two viruses( there are three of them in Pentaxim), so the impact of the vaccine on the body is more severe.
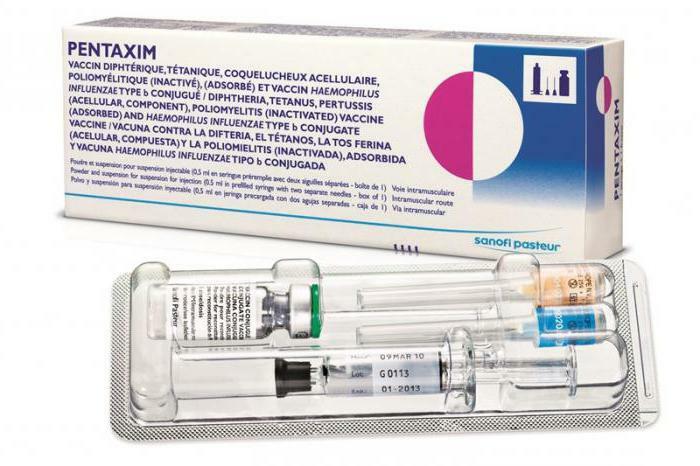
A live vaccine administered orally is not used, and therefore not produced in European countries. Live vaccine is produced in Russia, it includes a stabilizer( magnesium chloride) and three known strains of the virus. Poliovirus vaccination, the side effects of which may lead to the development of vaccine-associated poliomyelitis, requires the responsibility of the doctor and parents in the vaccination of the baby.
How to prepare a child for vaccination
Before the introduction of live virus, the child must undergo an examination with a pediatrician, where it will be decided whether it can be specifically given to him at the moment to be vaccinated. It is forbidden to vaccinate a child who lives in the same house with a pregnant woman, if she is not vaccinated.
Important! Vaccination from poliomyelitis for children taking immunosuppressive drugs or having congenital malformations of the gastrointestinal tract is strictly prohibited.
Also worth paying attention to the result of previous vaccinations - were there any side effects and how was the after-vaccination period.
After the introduction of the oral vaccine for an hour the child should not be given a drink or eat, in this case the vaccine will be destroyed and will not affect the formation of the child's immunity against poliomyelitis.
Poliovirus vaccine: side effects and health hazards
In case of timely and correct vaccination, side effects are rare and are negligible. It can be:
- general weakness of the body;
- slight increase in body temperature;
- redness and small swelling at the site of inoculation.
Symptoms after polio vaccination appear, usually after 1-2 days, and after a few days pass without any intervention.
In very rare cases when a live vaccine is administered, a vaccine-associated poliomyelitis can develop in a child. It is important to note that such consequences from vaccination arise only in the presence of a child's congenital immunodeficiency, malformations of the gastrointestinal tract, or the presence of AIDS in a person. In all other cases, vaccination against poliomyelitis is safe.
Contraindications to vaccination against poliomyelitis
Introduction of live oral vaccine is strictly prohibited when:
- has a malignant tumor;
- neurological disorders( in particular caused by previous vaccination);
- exacerbation of chronic diseases or the presence of acute diseases;
- immunodeficiencies( AIDS, HIV).
Vaccination is necessary for every child, but taking into account its individual characteristics. During the period of breastfeeding or pregnancy, a woman can be vaccinated against poliomyelitis if there is such a need. Whether to make a vaccine against poliomyelitis to your child, each parent decides on his own. But all the same it is better to overcome your fears and protect your baby from such a dangerous disease by timely vaccination.
