Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease( NAFLD): causes, signs, symptoms and treatment
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is an ailment that is accompanied by accumulation of lipid droplets in hepatocytes. Such a process affects the functioning of the body and can lead to dangerous complications. Unfortunately, the clinical picture is often fuzzy, and therefore the disease is diagnosed, as a rule, at the last stages of development.
Because pathology is common, many people ask questions about what is non-alcoholic hepatosis of the liver. Symptoms and treatment, causes and complications are important points that should be considered.
What is a disease? Brief description and etiology of
NAJBP, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is a very common pathology that is characterized by the accumulation of lipids in liver cells( hepatocytes).Since the droplets of fats are deposited inside the cells and in the intercellular space, there are abnormalities in the functioning of the organ. In the absence of treatment, the ailment leads to dangerous complications, increasing the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, cirrhosis or the formation of a malignant tumor in the liver.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is a problem of the present. According to research, the prevalence of the disease is about 25%( in some countries and up to 50%).True, statistics can hardly be called accurate, because it is rarely possible to diagnose an ailment on time. By the way, men, women, and even children are inclined to it. Mostly from the disease suffer in developed countries, which is associated with office, fixed lifestyle, constant stress and malnutrition.
The main reasons for the development of fatty disease

The question of why and how non-alcoholic fatty liver disease develops is still being studied in many research centers. But over the past few years, scientists have been able to identify several risk factors:
- Overweight( most patients with this diagnosis suffer from obesity).
- On the other hand, fatty hepatosis can develop and against the background of a sharp loss of weight, because this phenomenon is accompanied by a change in the body level of fats and fatty acids.
- Risk factors include diabetes, especially the second type.
- The risk of developing a disease in people with chronic hypertension is increased.
- NAJBP may appear against a background of increased triglycerides and cholesterol levels in the blood.
- Some drugs, in particular antibiotics and hormones( contraceptive pills, glucocorticosteroids) are potentially dangerous.
- Risk factors include malnutrition, especially if the diet contains dishes rich in easily digestible carbohydrates and animal fats.
- The disease develops against the backdrop of diseases of the digestive tract, including dysbacteriosis, ulcerative lesions of the machine, pancreatitis, impaired digestibility of nutrients in the walls of the intestine.
- Other risk factors include gout, pulmonary diseases, psoriasis, lipodystrophy, oncological diseases, heart problems, porphyria, severe inflammation, accumulation of a large number of free radicals, pathology of connective tissue.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: classification and development stages of
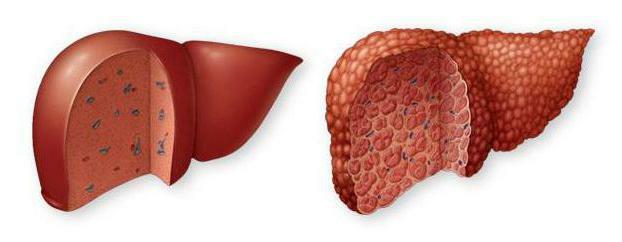
There are several ways to qualify the disease. But more often doctors pay attention to the location of the process. Depending on the place of accumulation of lipid droplets, focal disseminated, expressed disseminated, diffuse and zonal forms of hepatosis are isolated.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease develops in four stages:
- Obesity of the liver, in which there is accumulation of a large number of lipid droplets in the hepatocytes and intercellular space. It should be noted that in many patients this phenomenon does not lead to serious damage to the liver, but in the presence of negative factors, the ailment can pass to the next stage of development.
- Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, in which the accumulation of fat is accompanied by the appearance of an inflammatory process.
- Fibrosis is the result of a prolonged inflammatory process. Functional hepatic cells are gradually replaced by connective tissue elements. Scars are formed that affect the functioning of the organ.
- Cirrhosis is the final stage in the development of fibrosis, in which most of the normal liver tissue is replaced by scars. The structure and work of the organ is disturbed, which often leads to hepatic insufficiency.
What symptoms are accompanied by ailment?
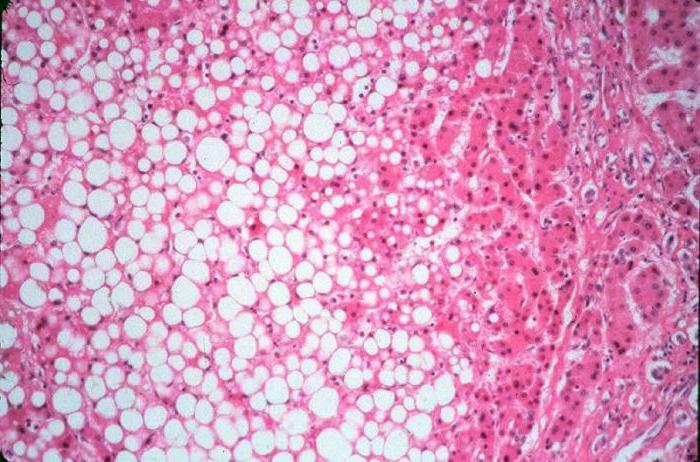
Many people are faced with a diagnosis of "non-alcoholic hepatosis of the liver."Symptoms and treatment are the issues that patients are most interested in. As already mentioned, the clinical picture of the disease is blurred. Often obesity of the liver tissues is not accompanied by severe disorders, which greatly complicates timely diagnosis, because patients simply do not seek help.
What signs accompany non-alcoholic fatty liver disease? Symptoms of the ailment are as follows:
- Because of irregularities in the liver, patients often complain of digestive disorders, in particular, nausea, heaviness in the abdomen that occurs after eating, a problem with the stool.
- Signs include increased fatigue, periodic headaches, severe weakness.
- In later stages of development, there is an increase in the size of the liver and spleen. Patients complain of severity and soreness in the right hypochondrium.
- Approximately 40% of patients can observe hyperpigmentation of the skin around the neck and underarms.
- Probably the appearance of vascular asterisks( mesh of dilated capillaries) on the palms.
- The inflammatory process is often accompanied by jaundice of the skin and sclera of the eyes.
Fat Disease in Children
Unfortunately, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is often diagnosed in children and adolescents. Moreover, over the past few days the number of such cases has increased significantly, which is associated with an increase in the level of obesity among underage patients.

The correct diagnosis is important here. It is for this during the planned school medical examinations that the doctors measure the parameters of the child's body, measure blood pressure, check the level of triglycerides and lipoproteins. These procedures provide an opportunity to diagnose the disease in time. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children may not require any specific treatment( especially if it is detected at an early stage).Correction of the diet and correct physical activity contribute to the normalization of liver function.
Diagnostic measures: laboratory tests
If a suspected pathology is suspected, laboratory tests are performed on the patient's blood samples. When studying the results of the analysis, it is worth paying attention to the following indicators:
- In patients, an increase in the activity of hepatic enzymes is observed. The increase is moderate, approximately 3 to 5 times.
- There is a disturbance in the metabolism of carbohydrates - patients suffer from impaired glucose tolerance, which corresponds to symptoms of type 2 diabetes.
- Another sign is dyslipidemia, which is characterized by an increase in the level of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood.
- Disturbance of protein metabolism and increase in bilirubin level is observed only in neglected cases.
Instrumental examination of the patient
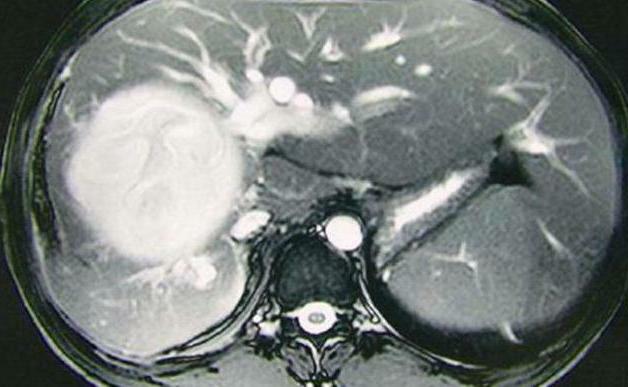
Further tests are carried out, in particular, ultrasound examination of the liver and abdominal organs. During the procedure, a specialist may notice areas of lipid deposition, as well as increased echogenicity. By the way, ultrasound is more suitable for diagnosing a diffuse fatty disease.
In addition, magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are performed. These procedures allow you to make a complete picture of the patient's condition and the degree of progression of the disease. By the way, with the help of tomography it is much easier to diagnose local foci of obesity of the liver.
Sometimes liver biopsy is necessary. A laboratory study of tissue images helps to determine whether there is an inflammatory process, whether fibrosis is heavily spread, what are the predictions for patients. Unfortunately, this procedure is rather complicated and has a number of complications, therefore it is carried out only in extreme cases.
Drug treatment of non-alcoholic hepatosis
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, despite the slow course, is dangerous, and therefore requires immediate treatment. Certainly, the scheme of therapy is made individually, since it depends on many factors.

As a rule, in the first place patients are prescribed the use of hepatoprotectors and antioxidants, in particular, preparations containing betaine, tocopherol acetate, silibinin. These drugs protect the liver cells from damage and slow the development of the disease. If the patient has insulin resistance, drugs that increase the sensitivity of the receptors to insulin are used. In particular, a positive effect is observed with the use of thiazolidinediones and biguanides. In the presence of serious disorders of lipid metabolism, lipid-lowering drugs are used.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: recommendations to patients
Since in most cases the disease is associated with obesity and metabolic disorders, patients are advised to follow a proper diet and get rid of excess weight. You can not allow a sharp loss of weight - everything needs to be done gradually.
Regarding the diet, first you need to start to slowly reduce the daily energy value of products. Fats in the daily diet should not be more than 30%.It is necessary to exclude products that raise the level of cholesterol, refuse from fried foods and alcohol. In the daytime menu you need to include foods with a lot of fiber, vitamin E and polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Part of the therapy is physical exercise. You need to start with the feasible exercises( at least walks) for 30-40 minutes 3-4 times a week, gradually increasing the intensity and duration of classes.
Is it possible to treat folk remedies?
Traditional medicine offers a lot of tools that can improve the functioning of the liver and release the body from toxins. For example, it is recommended to mix dry plantain leaves with honey in a ratio of 3: 1. Take a large spoon between meals 2 to 4 times a day. Within 40 minutes after consuming the medicine, it is not recommended to drink water and, of course, to eat.
A decoction of oats grains positively affects the liver. Since it is important to restore the patient's microflora, it is recommended to eat as much fermented milk as possible. It should be understood that self-medication with liver hepatosis can be dangerous. Any remedy can be used only with the permission of the attending physician.
