Ciliary body( ciliary body): structure and functions. Eye diagram
The vascular membrane responsible for the accommodation, adaptation and nutrition of the retina is a very important part of the eyeball structure. It consists of several parts, one of which is the ciliary body. Its composition includes many vessels and cells, the structure of which is peculiar to smooth muscle tissues.
These cells are arranged in layers, each of which has its own direction. Thanks to this, the necessary functionality of the ciliary body is achieved, which is to maintain a continuous supply of its own muscle fibers and to ensure the eye's ability to focus at different distances( accommodation).Another important function of the considered formation is the stabilization and maintenance of the required pressure inside the eyeball.
Structure of the eye: Anatomy
So what is the named part of the choroid, and what are its functions? To understand, you need to consider the structure of the eye. Anatomy distinguishes four main components in the visual organ:
- The peripheral part, called still perceiving( it consists of the eyeball itself, the eye's protective organs, the accessory organs and the muscular apparatus responsible for the movement of the eyeball).
- Conductive pathways consisting of the optic nerve, intersection and tract.
- Optical centers in the subcortex.
- Higher visual centers, which are located in the back of the cerebral cortex.
The eyeball is a very complex optical device, which is confirmed by the following diagram of the eye.
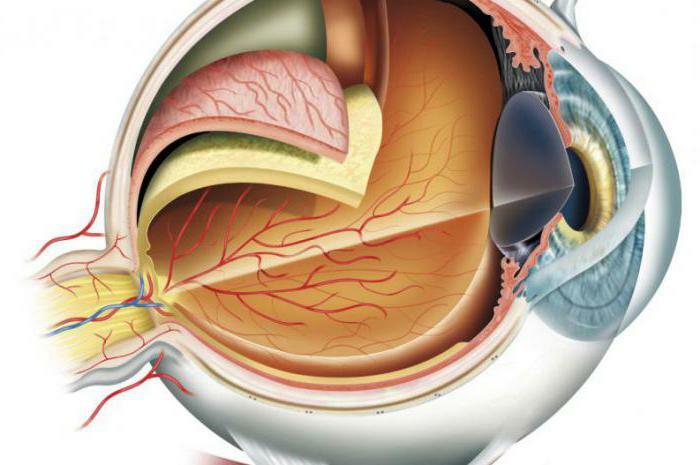
The main task of this organ is the transmission of the correct image to the optic nerve. And all the components of the eyeball are involved:
- cornea;
- anterior chamber of the eye;
- iris;
- pupil;
- crystalline lens;
- vitreous;
- retina;
- sclera;
- vascular membrane( in fact, part of it and is the ciliary body of the eye).
It is, as the diagram shows, between the sclera, the iris and the retina.
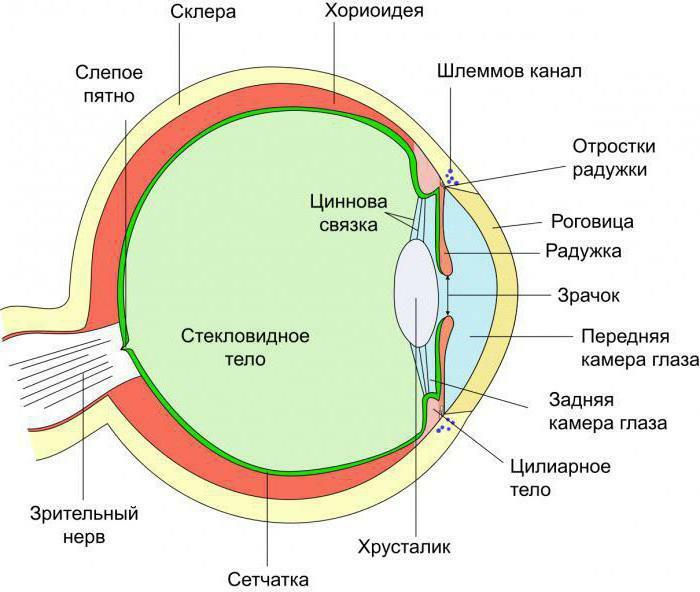
Ciliary body: structure and function
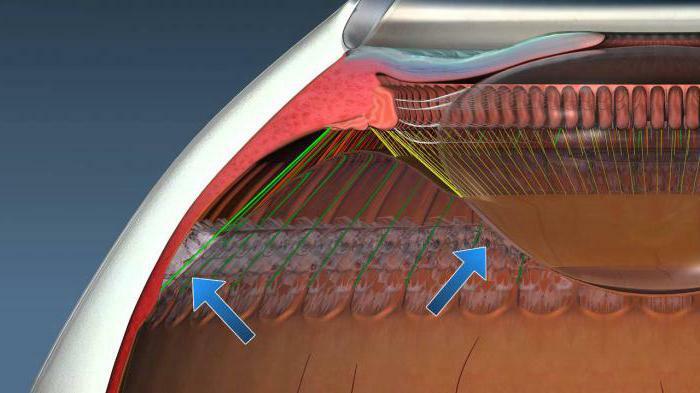
From the point of view of anatomy, the described part of the eyeball is a closed ring-shaped figure behind the iris, under the scleral membrane of the eye. This arrangement, by the way, does not allow a direct inspection of the ciliary body.
Considering the structural structure of this formation, we can distinguish two of its components: ciliary and flat.
- The first closely approaches the crenellated edge, and its width fluctuates around 4 mm.
- The second, ciliary, widths up to 2 mm. It is on it are special processes( ciliary or ciliary), which together represent a ciliary crown. They take a direct part in the formation of fluid inside the eye. This is due to the filtration of blood in a variety of blood vessels, which literally permeate each of the processes, which, incidentally, have a plate form.
Considering the ciliary body at the cell level, you can see that it consists of two layers: mesodermal and neuroectodermal. The composition of the first includes two types of tissue - connective and muscular. But neuroectodermal is limited to the presence of only epithelial cells, the presence of which is due to the spread of the latter from the retinal layer.
It turns out a kind of layered pie, the layers in which are as follows( from the deepest):
- muscular layer;
- vascular layer;
- basal membrane;
- pigment epithelium;
- epithelium without pigment layer;
- internal separating diaphragm.
Next, we will consider in detail the main components of the ciliary body, which includes the eye diagram.
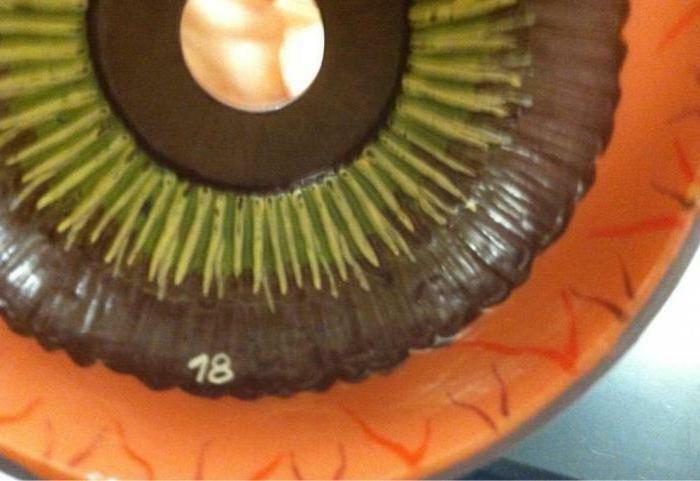
Muscle Layer
This layer is characterized by the presence of several muscles, going in different directions: longitudinal, radial and circular. Muscular fibers, called the Brueck muscles, differ in longitudinal direction, and are the outer part of the layer. Under them are the radially directed muscles of Ivanov. And the closing muscles are Muller's circular muscles.
The main task of each layer is to participate in the process of providing the eye's ability to clearly see at different distances( accommodation).There is it as follows. The inner part of the ciliary body communicates with the outer part of the lens( its capsule) through the ciliary belt, which consists of a large number of the finest fibers. The objective of this formation is to fix the lens in the right position, as well as to assist the ciliary muscle during accommodation processes.
Ciliated band fibers, called still zonal, are divided into two types: front and back. The first are attached to the equatorial and anterior region of the capsule of the lens, and the latter to the equatorial and, respectively, the posterior. Thanks to them, the tension and relaxation of the ciliary muscle is transferred to the lens membrane, and it becomes either more rounded or more elongated, which is the process of focusing the eye at a certain distance.
Vascular layer
The structure of this layer differs little from the structure of the choroid of the eye, the continuation of which it is. The composition of the vascular layer includes, for the most part, veins of various sizes. This is due to the fact that most of the arteries of the eye is located next to the choroid and, strangely enough, in the ciliary body, but in the muscular part. It is from there that small arterial vessels enter the vascular membrane.
Basal membrane
The continuation of the choroid of the eye is also this layer. From the inside it is covered with two kinds of epithelial cells: pigment and pigmentless. These types of cells are nothing but a non-functioning part of the retina. Behind them is the border membrane, which not only is the final layer of the ciliary body, but also separates it from the vitreous.
Physiological role of the ciliary body
Several basic functions of the ciliary body can be distinguished:
- Participation in accommodation processes, thanks to the ability to change the shape of the capsule of the lens using the muscle layer of the ciliary body. Accomodation provides accurate adjustment within 5 diopters.
- Providing a sufficient amount of intraocular fluid, due to the fact that the ciliary body contains a large number of vessels and, as a consequence, has a good blood supply. Subsequently, by means of this fluid, the pressure on the other components of the eyeball is necessary at a certain time.
- Maintain the right pressure inside the eye, which is one of the conditions for providing clear and clear vision.
- The vascular system involved in the supply of the ciliary body also nourishes the retina of the eye.
- The ciliary body acts as a support for the iris of the eye.

Pathologies of the ciliary body
In medicine, the diseases to which the ciliary body is exposed are:
- Glaucoma. In this case, the equilibrium between the synthesized intraocular fluid and its outflow is disturbed.
- Iridocyclitis. It is characterized by the appearance of inflammatory processes in the ciliary body.
- Reduced pressure inside the eye, due to a decrease in the volume of fluid in it. This can lead to swelling of the layers of the epithelium.
- Neoplasms in the ciliary body. In some cases, they may be of poor quality.
- Various pathologies of an innate nature.
When the first signs of a problem appear, you need to undergo a special examination that allows you to see the ciliary body of the eye, find out which pathological processes begin in it, and, if necessary, prescribe a treatment.
Result of
Summing up, it should be said again that the ciliary body, being a component of the choroid of the eye, is responsible for a number of important functions inside the eyeball. Among them - the normalization of pressure inside the eye and maintaining its balance, the synthesis of intraocular fluid, ensuring normal blood circulation in nearby tissues and, of course, participating in the accommodation process. It should be remembered that the diseases of the ciliary body will be reflected in the general state of human vision.
