Collagenosis - what is it? Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment of Disease
In modern medicine, there is often a diagnosis of "collagenosis".What it is? In fact, this term combines dozens of different diseases, which have one common feature - changes in connective tissue, in particular, fibrinoid collagen lesions.
Of course, patients diagnosed with "systemic collagenosis" panic. Therefore, first it is worth to learn more about such diseases and their peculiarities. What ailments are included in the group of collagenoses? What are the causes of their occurrence? What symptoms should I pay attention to? Can I get rid of collagen diseases forever? What predictions do doctors give? Many people are looking for answers to these questions.
Collagenosis: What is it?
Connective tissue, as is known, is a kind of building material for the body. For example, it forms the skeleton and human skin, the walls of blood vessels, the stroma of internal organs, and also fills the gaps between different structures. It is this tissue that makes up more than half the body weight of a person. Connective tissue elements perform a number of important functions, including trophic, protective, structural, supporting and plastic. It is the diseases of connective tissue that are united under the term "collagenosis".
What is it? This is a group of pathologies that have common signs and a development mechanism. Diseases develop against a background of immune homeostasis and are accompanied by fibrinoid changes in collagen.
Types of collagen diseases
Modern medicine is known for a variety of collagenases. Their classification is based on the origin of the disease. For example, diffuse connective tissue diseases can be congenital. To this group include syndromes of Stickler and Marfan, as well as mucopolysaccharidosis and imperfect osteogenesis. Symptoms of them, as a rule, appear in the period of intrauterine development.
There are acquired diseases that appear after birth - sometimes in childhood or adolescence, and sometimes even in adulthood. To this group of pathologies include systemic vasculitis, sceroderma, rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatism, eosovirus fasciitis, nodular periarteritis and many others.
The main causes of the disease
Congenital cases of the disease are associated with genetic disorders of metabolism and the structure of collagen. As for acquired forms of the disease, the reasons can be very diverse, and studies of the mechanism of development of pathologies are still under way.
Scientists tend to believe that there is genetic inheritance in almost every case. But there are many factors that can provoke the disease. For example, often a trigger is the penetration into the body of viral and bacterial infections, including causative agents of mumps, herpes, rubella measles, etc.
The causes may be hormonal bursts that are observed during puberty, pregnancy and menopause, after abortion,etc. There are other factors, under the influence of which the disease develops. Collagenosis can be caused by severe stress, trauma, medication, severe hypothermia, insolation. Sometimes the disease develops after vaccinations.
Pathogenesis of the disease
Despite the variety of diseases of this group, in almost every case the pathology develops according to the same scheme. Under the influence of this or that factor, the sensitization of the immune system occurs, as a result of which specific protein complexes are formed, which then settle on the serous and synovial membranes, the vascular membranes. The presence of immune complexes provokes allergic inflammation of tissues. Thus, the human immune system begins to attack its own connective tissues.
Against the background of the above processes, pathomorphological changes of tissues are observed. Of course, each type of collagenosis has specific features. For example, in scleroderma, an autoimmune inflammatory process affects the skin tissue and subcutaneous tissue, and nodular periarthritis is characterized by a change in blood vessels.
Collagenosis: photo and general clinical picture
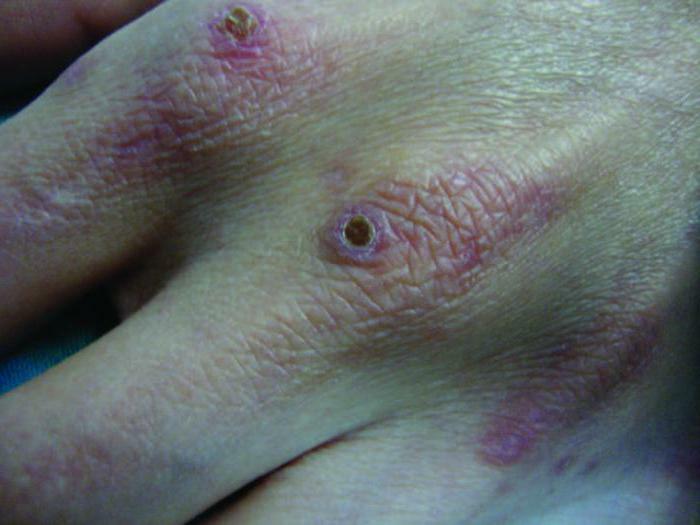
What does the clinical picture look like? What signs are accompanied by collagenosis? Symptoms, of course, will differ depending on the variety of the disease and the location of the inflammatory process. Nevertheless, some common features can be distinguished.
Patients have a persistent increase in body temperature up to 38 degrees. Patients complain of chills and excessive sweating. There is weakness and decreased efficiency. Practically for any form of collagen, joint-muscular syndrome develops, which is characterized by joint pain, myalgia and arthralgia. Sometimes there are allergic reactions, the appearance of rashes on the skin, abdominal pain, digestive disorders.
Nodular periarteritis and its features
Collagenoses are diverse in nature, so it is worth considering the most characteristic and severe varieties. Nodular periarteritis is characterized by the defeat of all three layers of the vascular wall. Almost all the vessels of the body are involved in the inflammatory process.
Symptoms depend on which arteries and veins were affected. If it is a question of the vessels of the kidneys, then patients first of all note pain in the lower back, violation of the outflow of urine. There is hypertension and progressive renal failure. When the walls of the cerebral vessels become inflamed, the patient develops various disorders of the psyche. A quarter of patients with nodular periarthritis have bronchial asthma.
Systemic lupus erythematosus
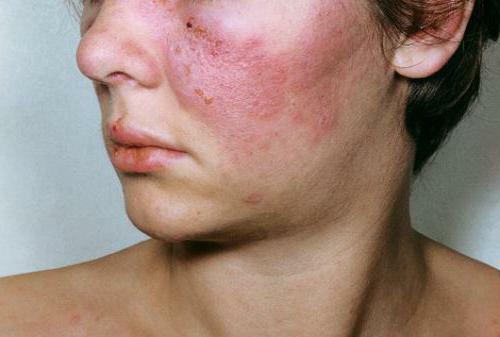
Lupus erythematosus - severe systemic collagenosis. What it is? This disease, which is accompanied by the defeat of almost all organ systems. On the skin appear reddish foci of inflammation( on the face they have a very characteristic location in the cheek and nose, which resembles the butterfly's wings).
Nails and hair are affected, ulcers and erosions appear on the mucous membranes. In the inflammatory process, small joints are involved. The disease is accompanied by violations from the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. Kidney pathologies and the appearance of neurologic symptoms are observed.
Systemic scleroderma
Scleroderma is another autoimmune disease in which the inflammatory process affects the skin, subcutaneous tissue, peripheral vessels, joints and muscles. The most obvious symptoms are skin changes. First, there is swelling of the skin. The dermis acquires a pale or, on the contrary, red shade. At the second stage of the disease, the edema becomes very dense, the patient's skin is smooth and dry, spikes with underlying tissues are formed.
The third stage is accompanied by atrophy of skin and subcutaneous tissues. The body of a sick person is exhausted, fingers are gradually deformed, the face takes on the form of a mask due to the disappearance of facial expressions.
Diagnostic process
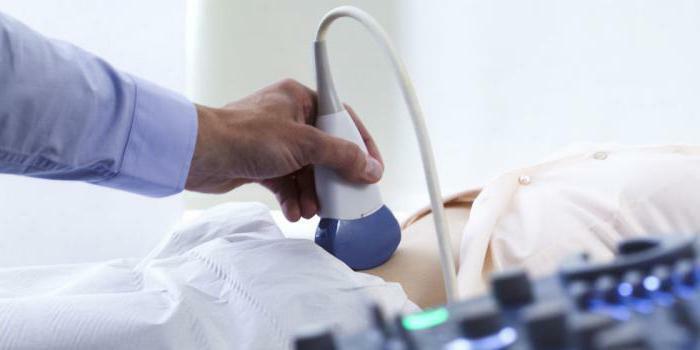
How is collagenosis diagnosed? The defeat of certain organs is accompanied by the appearance of very characteristic symptoms, which the specialist pays attention to during communication with the patient and collecting an anamnesis. Further, various laboratory tests are carried out. In particular, the blood of a sick person is checked for the presence of nonspecific inflammatory markers, namely: fibrinogen, C-reactive protein, alpha-2-globulins. A study is also conducted for the presence of immunological markers in the body, which are specific for each individual disease.
Often in order to fully assess the patient's condition, a biopsy is performed. The analysis takes samples of tissues of muscles, skin, kidneys, synovial membrane of the joints.
There are also instrumental studies helping to determine such a disease as collagenosis. Diagnosis includes X-ray examination of joints and bones. In the pictures, the doctor may notice the characteristic signs of some connective tissue lesions, including osteoporosis, articular surface changes and their aseptic necrosis, narrowing of joint slots, etc.
Since collagenoses are often accompanied by internal organ damage, an important procedure is ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs, kidneys, pleural cavity, heart( echocardiography).Additionally, computer or magnetic resonance imaging is used to evaluate the condition of the body, as well as damage to internal organs and the skeleton.
Medication for collagen diseases

What therapies require collagenoses? Treatment of diseases of this group must necessarily be complex. Scheme of therapy is made individually, because it depends on the form and stage of development of the disease, the presence of concomitant diseases, the age of the patient.
Since inflammatory lesions of connective tissue structures are observed with collagenoses, first of all, patients are prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs. In the early stages of development, non-steroidal drugs, in particular those containing ibuprofen, are effective.
In those cases, if the disease progresses very quickly, glucocorticosteroid preparations with more pronounced anti-inflammatory properties are introduced into the regimen of therapy. As a rule, "Prednisolone" is used( the maximum daily dose is not more than 15 mg).
Cytostatic drugs( "Azathioprine", "Cyclophophamide") give good results. Such therapy is carried out in the event that reception of steroids has not given expected effect or has caused serious adverse reactions.
Treatment of an illness during an exacerbation is spent in the conditions of a hospital. The patient is discharged from the hospital only after he has managed to cope with the main symptoms. It is very important to adhere to the correct mode of work and rest, as well as to monitor nutrition, not only during a period of exacerbation, but throughout life.
Other therapies
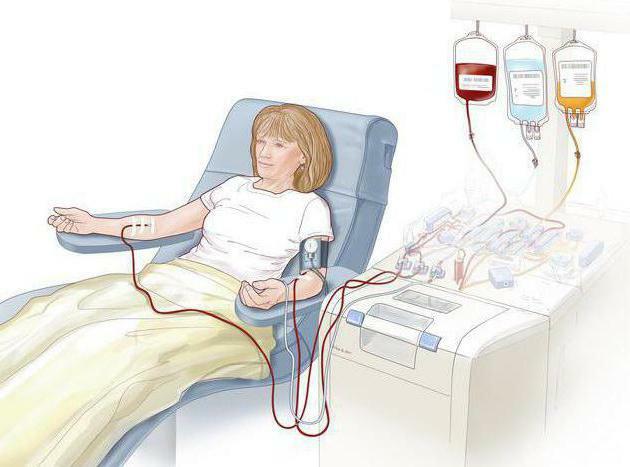
What other therapies require collagenoses? Treatment is necessary not only during an exacerbation, but also during the relative well-being of the body. In order to slow the progression of the disease, hemocorrection methods, in particular hemosorption and plasmapheresis, are used. Some patients are also recommended physiotherapy. Quite good results can be achieved with the help of regular courses of magnetotherapy, drug electrophoresis, ultraphonophoresis.
With rheumatoid arthritis and a number of other diseases, therapeutic exercise will help, which will help maintain normal mobility. Patients are recommended regular sanatorium treatment in institutions of the appropriate profile. With some collagen diseases a good effect is provided by radon, hydrogen sulphide and carbon dioxide baths. Of course, the therapy scheme is determined by the doctor depending on the variety of the disease, age and condition of the sick person.
Prophylactic measures and predictions for patients
Collagen disease( any of its varieties) is characterized by progressive, chronic course. Drug therapy makes it possible to reduce manifestations of the disease and to achieve a more or less prolonged remission. Nevertheless, it is almost impossible to completely stop the disease. Especially dangerous are systemic collagenoses, which often end with the development of acute respiratory or heart failure.
Admission of hormones and immunomodulators is certainly important. But patients should monitor their health and remission, as this will help to stave off a new exacerbation. Patients are advised to avoid the effects of provoking factors, be they severe stresses and hormonal disruptions, or severe supercooling and excessive insolation. If you have any infectious disease, you need to see a doctor immediately. Foci of chronic inflammation should also be amenable to adequate therapy.
