Fractures of the radius in a typical place: description, symptoms and features of treatment
A fracture is a bone injury that occurs with a partial and complete disruption of its integrity under the influence of a traumatic factor. Fractures of the radius in a typical place - ordinary pathology for a traumatological hospital. Actually, that's why she was given such a "talking" name. Particularly common is the trauma of the distal part, the one that is closer to the wrist. 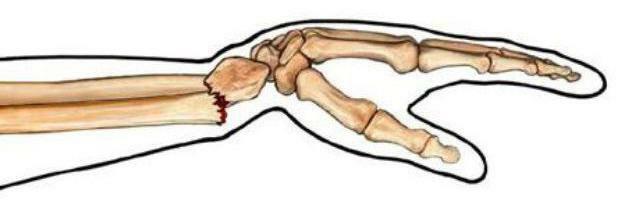
Anatomy
Normally, the forearm is formed by two bones located parallel to each other: radial and ulnar. They can rotate around a long or longitudinal axis, because they are connected to each other by two moving joints and a membrane:
- Elbow joint. Combines the bones at the point of their connection with the shoulder.
- Interosseous membrane. It is located in the space between the radial and ulnar bones, in it are the vessels and nerves that feed the forearm. In addition, it is a kind of separator for some muscles of the forearm.
- Wrist joint. It has ligaments that connect the radial and ulnar bones.
As a single structure, the forearm includes not only bones, but also ligaments, joints, muscles, vessels and nerves.
Bones and Joints
Since the radial and ulna are tubular, it is necessary to know their structure in order to better understand the details of the fractures. So, each long tubular bone has:
- Epiphysis is an extension of the bone to form an articular surface. It is formed by a porous spongy substance and contains a red bone marrow.
- Metaphysis is a small area of the bone, which is characterized by rapid cell division. It is thanks to him that we grow.
- Diaphysis is the main long bone. It is a hollow tube constructed of a dense substance. Inside it is the yellow bone marrow.
Above, each tubular bone is covered with a periosteum, which nourishes the base material, provides its thickening and has a large number of nerve endings. Often this feature helps to diagnose fractures, because the bone of pain receptors itself is deprived. 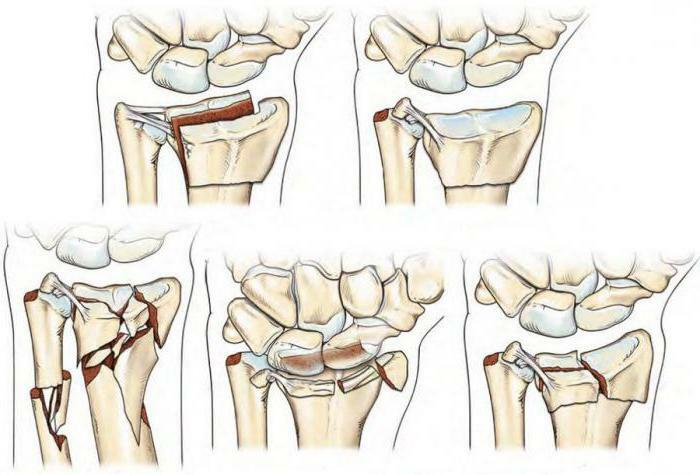
Joints are only two, but they are complex in structure because they are formed by three or more bones:
- The elbow joint is formed by the radial, ulnar and humerus bone, it can perform flexion, extension and limited amplitude rotation.
- Wrist joint - contains the lower segment of the radius and the upper row of wrist bones. The volume of movements is wide enough.
Muscles
To provide such a variety of movements requires a large number of muscles. And they need to be thin enough, but at the same time strong and elastic. All the muscles of the forearm are divided into:
1. Flexors: located on the front surface of the forearm. There are superficial and deep. The fixation point for them is the lower end of the humerus, and the point of movement is the bones of the wrist and the phalanges of the fingers. Their function is to bend the hand and fingers.
2. Extensors: located on the back of the forearm. They are responsible for the extension of the hand and fingers. The attachment points are the same for them.
3. Muscles that rotate the forearm: Detected between the radial and ulna bones.
All muscle groups are graceful and have long, thin tendons passing through the wrist. Thus, with injuries to the forearm, a small effort is enough to damage the motility of the movements due to damage to the muscular framework.
Vessels and nerves
Large vessels flow through the forearm, the damage of which leads to rapid loss of blood and serious consequences for the body. These are branches of the brachial artery, which are divided in the region of the ulnar fossa into the radial and ulnar fossae.
The first provides nutrition to the muscles of the forearm, as well as the hand and fingers from the palm. It is on it that the doctors feel the pulse.
The second is parallel to the beam. It gives away many branches that weave into the muscular fascia and nourish them. Forms a deep arterial arch of the hand.
The veins on the forearm, like the rest of the body, are divided into superficial and deep. According to its name, the first go directly under the skin, and the second accompany the same veins.
The innervation of the forearm is carried out from the brachial plexus. From it depart sensitive and motor branches. The largest of them are the ulnar nerve( controls the flexors and the medial part of the palm), the radial( responsible for the flexors) and the median( involved in the regulation of the brush).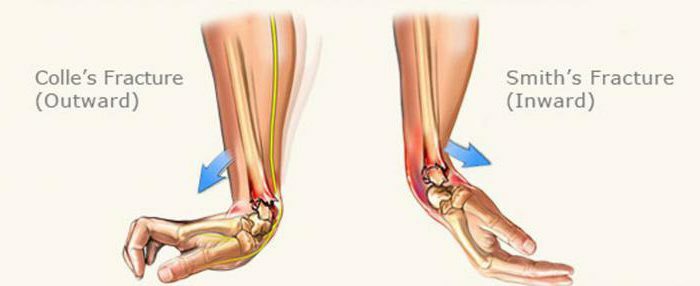
Types and types of fractures
It is known from the school course of physics that a fracture appears in the place where excessive force was applied. But this factor alone is not enough. It is also necessary to reduce the strength of the bone and a certain point of application of the kinetic energy. This principle was the basis for the classification of all types of fractures.
- Pathological. When the force directed to the bone is low, but because of the reduction in strength, it still breaks. This is due to genetic( syndrome of the crystal child), metabolic or endocrine pathologies, as well as to the growth processes of malignant neoplasms. Increased fragility can also be a manifestation of age, when the elderly are disturbed by calcium-phosphorus metabolism.
- Traumatic. When the intensity of force exceeds the density of bone tissue. As a rule, this is the result of accidents, road accidents, sports injuries. During the fall, a person instinctively puts forward his hand, trying to protect his face or chest, and the entire blow falls on the wrist and forearm.
According to statistics, traumatic fractures are more common, they are more dangerous, as a result, besides the bone, vessels, nerves, and muscles can be damaged. The risk of disability is very high.
On the mechanism of education, fractures are:
- Transverse - when the application force is perpendicular to the axis of the bone.
- Skew - the direction of the action of the force is at an angle. It can occur both with direct exposure to a part of the body, and indirectly.
- Screw-shaped - if the bone was subjected to a strong rotation at a fixed one end. For example, during an accident.
- Longitudinal - the fracture line is parallel with the bone length. Usually appear with a strong squeezing and impact blunt object with an unlimited surface( asphalt, earth).
- Splintered - there are more than two bone fragments, there is no clear fracture line.
- Embedded - arise when falling from a height. The direction of the force passes along the longitudinal axis of the bone, and after fracture the fragments "enter" one into the other.
For any of these lesions, bone fragments can be displaced and additional trauma of soft tissues can occur. But fractures of the radius in a typical place usually do without small fragments.
There is one more classification, indicating the degree of skin damage. It divides all fractures into open and closed ones. Open, as it would be logical to assume, damage the skin, and bone fragments can be seen with the naked eye. They are dangerous because of the high probability of infection of the wound and significant blood loss. Closed fractures have a more favorable course and do not communicate with the external environment. 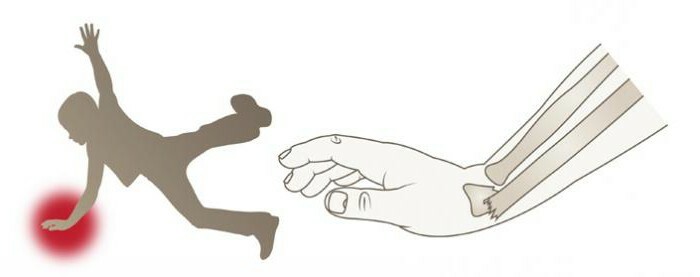
Localization of
The trauma doctor, knowing where the fractures most often occur, can accurately diagnose the trauma. So:
- Area of the head and neck of the radius, next to the elbow joint. Formed by falling on an outstretched arm.
- Diaphysis of the radius - happens with excessive force. Often combined with a fracture of the ulna.
- A fracture of a radius in a typical place is in three centimeters from a brush. Occurs when falling on a bent brush with an outstretched arm. It is more common in older women because of postmenopausal osteoporosis.
- Fracture with a dislocation of the ulna.
Symptoms of
It is clear that the main complaints of a person who has a bone fracture diagnosed in a typical place do not differ from those for another lesion localization, but nevertheless one should emphasize the symptoms.
So, the patient in the waiting room will complain of pain in the area of the injury, which is aggravated by pressure and movement. There is a pathological mobility of the injured forearm, if there has been a displacement of fragments or fragmentation of the bone. Because of the swelling, there will be swelling of the hand and a symptom of fluctuations. The damage of large vessels is often said to be a hematoma. In addition, after the injury, there may be a visually or instrumentally determined limb shortening( due to displacement of bone fragments), as well as a crepitation symptom( crunch) when trying to probe the injury site. Closed fracture of the radius in a typical place is characterized by deformation and defoguration of the wrist joint with pathological flexion or extension of the hand, displacement of the fragments and disturbance of the wrist relief. 
Diagnostics
Consists of several stages:
- Poll( complaints, mechanism of injury, medical history and health).
- Inspection( skin color, presence of fluid under it, pulse, degree of damage and pathological passive and active movements in the fracture site).
- Radiography( a picture of a damaged limb in two projections).
- Tomography linear and computer( it is used in especially difficult cases to exclude a mistake in diagnosis or prepare for a reconstructive operation).
- Angiography( done to exclude damage to the vessels of the forearm).
Emergency care
Since fractures of the radius in a typical place are quite common, it is not superfluous to tell about first aid to the victims.
- Be sure to call the ambulance.
- Maximum immobilize the limb to prevent the displacement of fragments.
- Apply cold to the fracture site, but do not forget to wrap a piece of ice in the towel so that there is no frostbite.
- Drink anesthetic.
Most often, a fracture of the right radial bone occurs in a typical place, since this hand is working in most people. A person instinctively tries to be shielded by it or leaned and traumatized. However, do not forget that a fracture of the left radial bone in a typical place is also possible( both in right-handed and left-handed).It all depends on the situation. Therefore, doctors should not lose their vigilance. 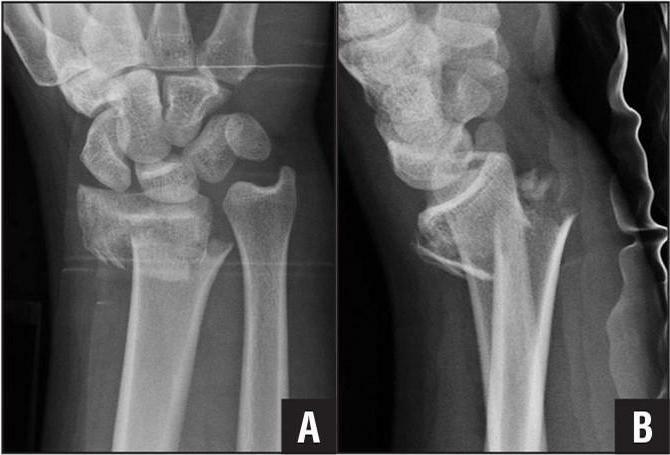
Treatment of
The basis of therapy, as in other cases, is limb immobilization and relief of pain syndrome. To do this, use a plaster bandage or langets, taking pain medications. But the treatment of fracture of the radius in a typical place does not end there. The sufferer must be vaccinated against tetanus, given antibiotics and immunoglobulins to increase the body's resistance( especially appropriate with open fractures).Wearing gypsum lasts up to 2-2,5 months. Surgery may be required if complications occur. 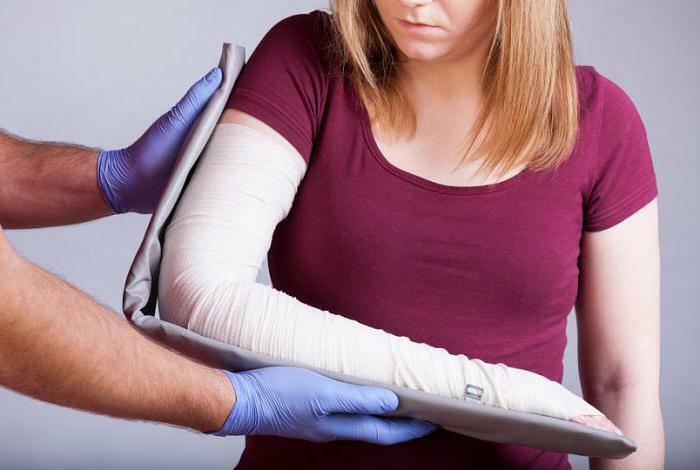
Complications of
No one is immune from problems even with such a common phenomenon as a fracture of the radius in a typical place. Complications usually appear at the diagnostic stage. These include:
- open fracture;
- additional fracture of the ulna;
- presence of dislocation or subluxation;
- significant displacement of fragments;
- nerve compression or vascular injury;
- pathological fracture;
- is a multi-lobed fracture.
Restoring
The next step after the removal of gypsum is a long process of physiotherapy, which is necessary to restore the function of the forearm and hand. Usually this happens 2-3 months after the diagnosis of "fracture of the radius in a typical place."Rehabilitation is necessary to strengthen the muscular framework of the limb and gradually restore its mobility after a prolonged immobilization. Difficulties can arise in elderly people, patients with diabetes mellitus, impaired liver function, kidneys and reduced immunity.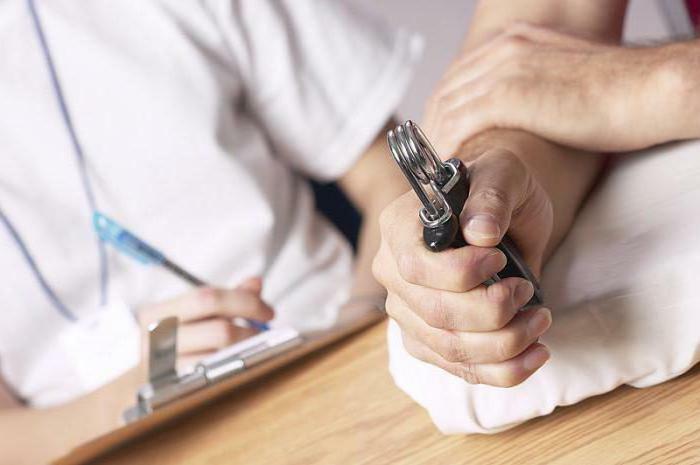 
Fractures of the radius in a typical place - a fairly ordinary and routine diagnosis in the emergency room, but from this pathology is not becoming less important for either the doctor or the patient.
