Agglutinin and agglutinogen are blood proteins that save life
Agglutinogen is a protein of blood. Antigens are formed already in the third month of fetal development. It is present in the composition of 2, 3 and 4 blood groups. It is known, according to modern data, about 236 antigens, which are stored in 29 systems. The blood group is determined based on 2 systems - ABO and Rhesus factor.
Composition of blood. Agglutinogen is what?
As is known, the blood consists of water, plasma and also the elements: leukocytes, erythrocytes and platelets.
Agglutinogens are also called antigens( AH).They are present in all cells of the body. Their protection is necessary everywhere. Even in the brain. Antigens are also found on the inner surface of red blood cells. Their agglutinogens have and leukocytes( more than 90 species).
Agglutinogen is a chemical that stores and identifies a genetically alien information for a particular individual and interacts with antibodies.
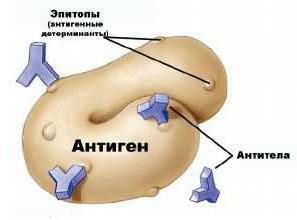
By their chemical nature, they are divided into:
- proteins( Rh-protein, Colton, etc.);
- glycoproteins( Lutheran);
- glycolipids( ABO).
Agglutinogen is a gamma globulin that is transmitted to a newborn by inheritance. He, along with the agglutinin present in the plasma, determines the blood group, as will be discussed below.
Functions of agglutinogens and agglutinins
If agglutinogens, the same antigens, are obtained from the parents, then agglutinins( antibodies or AT) are produced during the first year of life of the child. The antibody synthesizes the immune system, and they interact only with the antigen for which they are intended.
It's the antibodies that cause the immune response. They agglutinate( or simply put, glue) the cells of microbes and so destroy them. Then these lumps with dead alien cells are precipitated and simply removed from the body. And antigens give them all the necessary information. So agglutinogens, agglutinins of blood save the body from the invasion of foreign bodies. Without their work, survival in an environment is impossible.
Blood groups
Distinguish groups by the presence or absence of antigens and antibodies. There are a lot of antigens. However, antigen A and B, as well as antibodies Alpha and Beta, are most important for doctors.
The second important characteristic of human blood is the Rh-protein of blood, i.e., its presence or absence.
| Group | Agglutinogenes( AG) | Agglutinins( AT) |
| 1 | - | alpha and beta AT |
| 2 | A | beta AT |
| 3 | B | Alpha AT |
| 4 | A, B | - |
So distinguish blood groups;agglutinogens and agglutinins are taken for classification only those that are related to agglutination.
To determine the group, conduct such an experiment. When the blood serum is mixed, an agglutination reaction occurs( or does not occur).This is the conclusion they make.
Agglutination is a reaction in which antibodies and antigens that are not compatible with each other coalesce and break down. For example, agglutinogens of erythrocytes of the 2nd blood group are combined with Beta antibodies in plasma. If Alpha antibodies get into this blood, they will be glued together. The cells die. And the ingested Beta antibodies in a test tube with serum, which has antigen B, will also "launch" the above reaction.
History of research
Blood groups were first distributed according to the ABO system. This happened in 1901, when K. Landsteiner discovered antibodies. Classification was developed by K. Landsteiner and J. Yansky. They came to the conclusion that agglutinogen is that particle, without knowing the characteristics of which it is impossible to continue experiments with transfusion. And we continued to work in this direction. In 1903, four groups were singled out.
And in 1940, A. Wiener and K. Landsteiner discovered the Rh factor. This protein occurs in about 85% of people with white skin color. If the protein is present in the blood, it is a positive Rh( Rh +), and when there is no - a negative( Rh-).Since then, the blood group is classified on the basis of 2 of these systems.
Transfusion rules
Blood transfusion even in our time, with all the medical knowledge of our century, is dangerous. Transfusion is used only when the blood loss is 25% or more of the total. There are many dangers - viruses, posttransfusion shock - anything.
Try to find the most suitable blood, otherwise blood transfusion complications may occur. Although it is generally known that people with one group - donors are universal, yet if the volumes of the transfused blood are rather large, it is better to abandon another blood group. The same applies to people with group 4, who are recipients of other groups.
Carriers of the 1st group are due precisely to this and are called universal donors, that there are no blood agglutinogens that are meaningful for transfusion. After all, there will not be an agglutination reaction in this case.

In general, the rules of transfusion are simple. But still no one can say the consequences of the transfusion. In the blood there may be hidden agglutinogens, and in the analysis there is a likelihood that they will not be detected. Then the person after transfusion of large volumes of blood will die of shock. Nevertheless, one's group needs to know exactly every person and, of course, to know the presence of Rh-protein.
Rh factor and pregnancy
If a woman has a negative Rh blood protein, it means that pregnancy can have problems. A child with the presence of this protein will be an alien object to the mother's body.
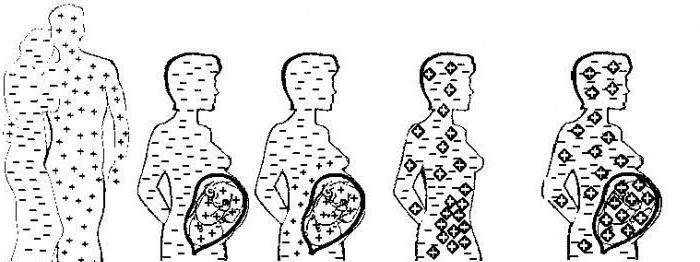
Once upon a time, women were even advised not to marry a man who had Rh-protein. Mother's antibodies will destroy the red blood cells of the fetus. After all, every agglutinogen is part of the "system of attack" on cells, which seem alien to them.
In case of a rhesus conflict, such complications are possible:
- hemolytic disease in a child;
- jaundice at birth;
- miscarriage.
Still, if a woman takes care of herself and is constantly under the control of doctors, the child will be born quite healthy.
